Two outer membrane proteins are bovine lactoferrin-binding proteins in Mannheimia haemolytica A1
- PMID: 27599994
- PMCID: PMC5013584
- DOI: 10.1186/s13567-016-0378-1
Two outer membrane proteins are bovine lactoferrin-binding proteins in Mannheimia haemolytica A1
Abstract
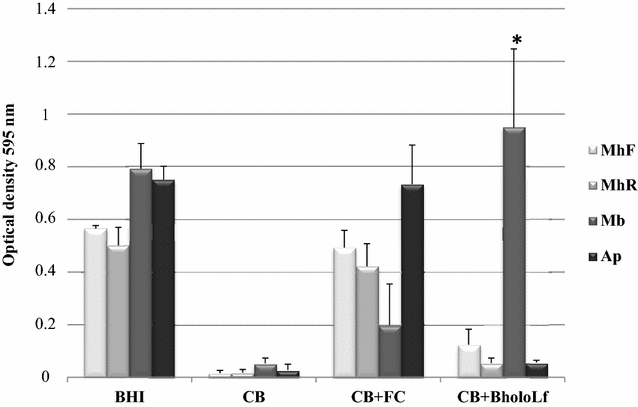
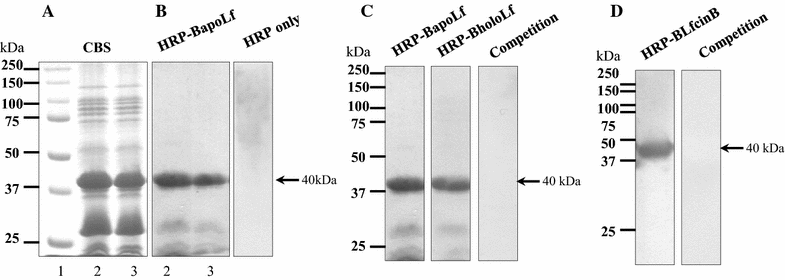
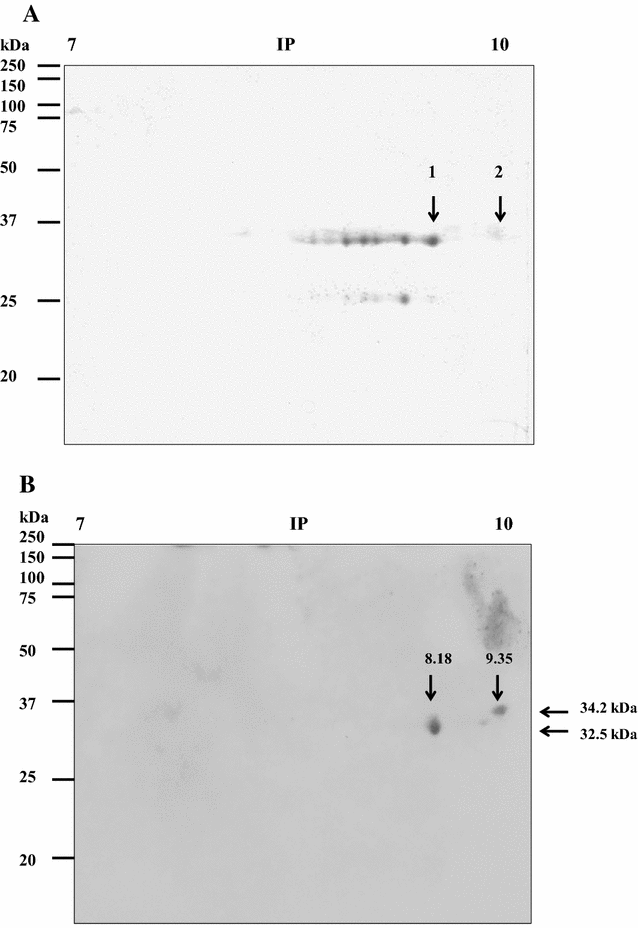
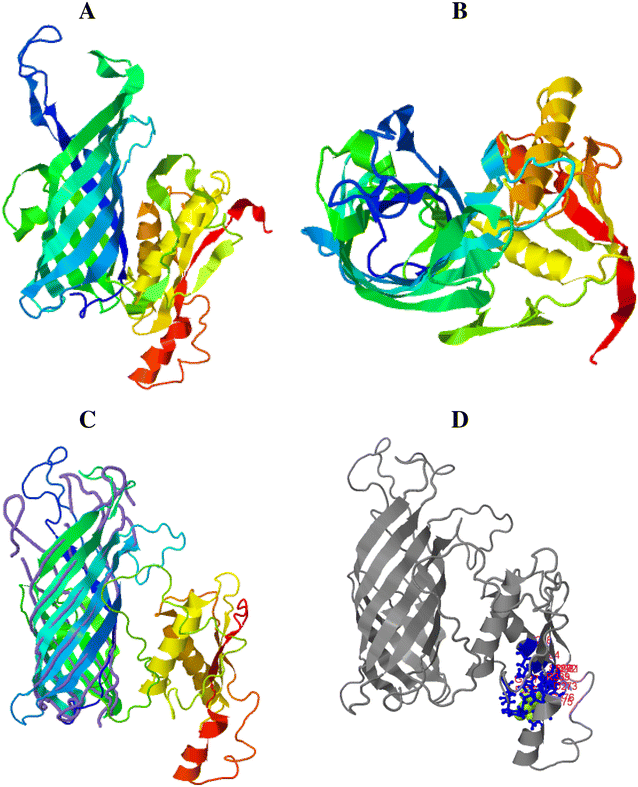
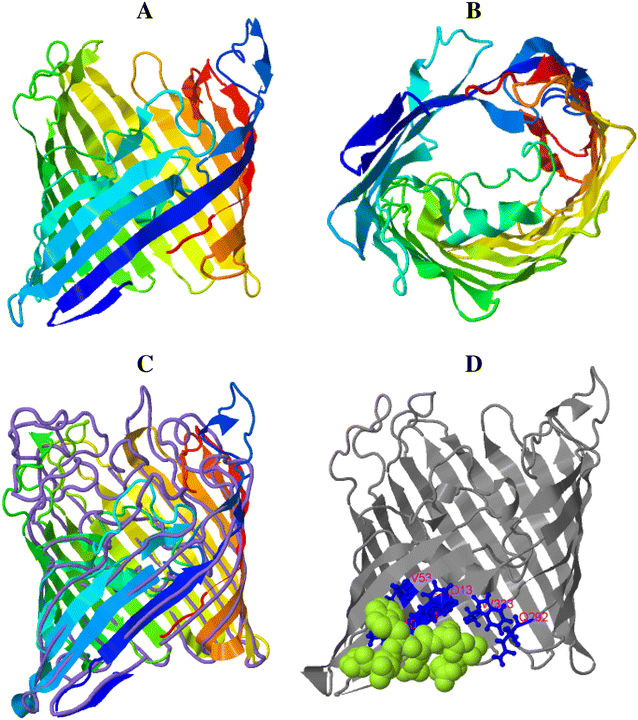
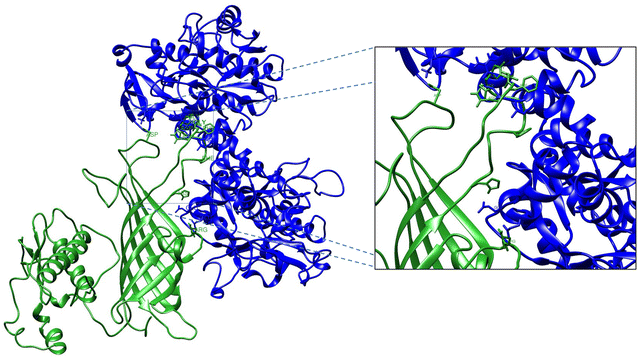
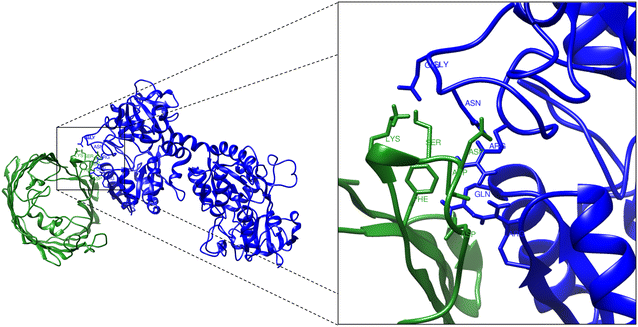
Mannheimia haemolytica is a Gram negative bacterium that is part of the bovine respiratory disease, which causes important economic losses in the livestock industry. In the present work, the interaction between M. haemolytica A1 and bovine lactoferrin (BLf) was studied. This iron-chelating glycoprotein is part of the mammalian innate-immune system and is present in milk and mucosal secretions; Lf is also contained in neutrophils secondary granules, which release this glycoprotein at infection sites. It was evidenced that M. haemolytica was not able to use iron-charged BLf (BholoLf) as a sole iron source; nevertheless, iron-lacked BLf (BapoLf) showed a bactericidal effect against M. haemolytica with MIC of 4.88 ± 1.88 and 7.31 ± 1.62 μM for M. haemolytica strain F (field isolate) and M. haemolytica strain R (reference strain), respectively. Through overlay assays and 2-D electrophoresis, two OMP of 32.9 and 34.2 kDa with estimated IP of 8.18 and 9.35, respectively, were observed to bind both BapoLf and BholoLf; these OMP were identified by Maldi-Tof as OmpA (heat-modifiable OMP) and a membrane protein (porin). These M. haemolytica BLf binding proteins could be interacting in vivo with both forms of BLf depending on the iron state of the bovine.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of apo-lactoferrin on leukotoxin and outer membrane vesicles of Mannheimia haemolytica A2.Vet Res. 2020 Mar 5;51(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s13567-020-00759-z. Vet Res. 2020. PMID: 32138772 Free PMC article.
-
Apo-Lactoferrin Inhibits the Proteolytic Activity of the 110 kDa Zn Metalloprotease Produced by Mannheimia haemolytica A2.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 28;25(15):8232. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158232. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125801 Free PMC article.
-
Serum antibody responses of cattle to iron-regulated outer membrane proteins of Pasteurella haemolytica A1.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1995 Jul;47(1-2):101-10. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(94)05390-e. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1995. PMID: 8533287
-
[Mannheimia haemolytica and the pathogenesis of enzootic bronchopneumonia].Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2004 Mar-Apr;117(3-4):97-115. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2004. PMID: 15046457 Review. German.
-
Mannheimia haemolytica in bovine respiratory disease: immunogens, potential immunogens, and vaccines.Anim Health Res Rev. 2018 Dec;19(2):79-99. doi: 10.1017/S1466252318000142. Anim Health Res Rev. 2018. PMID: 30683173 Review.
Cited by
-
Phenotypic and genotypic assessment of iron acquisition in diverse bovine-associated non-aureus staphylococcal strains.Vet Res. 2024 Jan 12;55(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s13567-023-01260-z. Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 38217046 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Killing of Pathogenic Escherichia coli Using Camel Lactoferrin from Different Saudi Camel Clans and Various Antibiotics.Protein J. 2019 Aug;38(4):479-496. doi: 10.1007/s10930-019-09828-5. Protein J. 2019. PMID: 30963371
-
Bovine apo-lactoferrin affects the secretion of proteases in Mannheimia haemolytica A2.Access Microbiol. 2021 Oct 25;3(10):000269. doi: 10.1099/acmi.0.000269. eCollection 2021. Access Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34816089 Free PMC article.
-
Antigenicity analysis of the recombinant outer membrane NlpI protein of Mannheimia haemolytica.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):22401. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05125-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40596169 Free PMC article.
-
Lactoferrin: Balancing Ups and Downs of Inflammation Due to Microbial Infections.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Mar 1;18(3):501. doi: 10.3390/ijms18030501. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28257033 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jaramillo-Arango C, Hernandez-Castro R, Suarez-Guemes F, Martinez-Maya J, Aguilar-Romero F, Jaramillo-Meza L, Trigo F. Characterisation of Mannheimia spp. strains isolated from bovine nasal exudate and factors associated to isolates, in dairy farms in the Central Valley of Mexico. Res Vet Sci. 2008;84:7–13. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2007.03.008. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

