Reverse Phase Protein Arrays-Quantitative Assessment of Multiple Biomarkers in Biopsies for Clinical Use
- PMID: 27600215
- PMCID: PMC4996393
- DOI: 10.3390/microarrays4020098
Reverse Phase Protein Arrays-Quantitative Assessment of Multiple Biomarkers in Biopsies for Clinical Use
Abstract
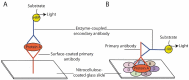
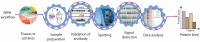
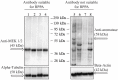
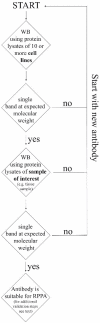
Reverse Phase Protein Arrays (RPPA) represent a very promising sensitive and precise high-throughput technology for the quantitative measurement of hundreds of signaling proteins in biological and clinical samples. This array format allows quantification of one protein or phosphoprotein in multiple samples under the same experimental conditions at the same time. Moreover, it is suited for signal transduction profiling of small numbers of cultured cells or cells isolated from human biopsies, including formalin fixed and paraffin embedded (FFPE) tissues. Owing to the much easier sample preparation, as compared to mass spectrometry based technologies, and the extraordinary sensitivity for the detection of low-abundance signaling proteins over a large linear range, RPPA have the potential for characterization of deregulated interconnecting protein pathways and networks in limited amounts of sample material in clinical routine settings. Current aspects of RPPA technology, including dilution curves, spotting, controls, signal detection, antibody validation, and calculation of protein levels are addressed.
Keywords: FFPE; antibody; cancer; diagnostics; personalized medicine; protein; therapy; tissue.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical utility of reverse phase protein array for molecular classification of breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016 Jan;155(1):25-35. doi: 10.1007/s10549-015-3654-2. Epub 2015 Dec 9. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2016. PMID: 26661092
-
Molecular profiling of signalling pathways in formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded cancer tissues.Eur J Cancer. 2010 Jan;46(1):47-55. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2009.10.016. Eur J Cancer. 2010. PMID: 19914823 Review.
-
Use of formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded tissues for diagnosis and therapy in routine clinical settings.Methods Mol Biol. 2011;785:109-22. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-286-1_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21901596
-
Protein microarray-based comparison of HER2, estrogen receptor, and progesterone receptor status in core biopsies and surgical specimens from FFPE breast cancer tissues.Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2011 Jul;19(4):300-5. doi: 10.1097/PAI.0b013e3182054f9f. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2011. PMID: 21293257
-
Analysis of Reverse Phase Protein Array Data: From Experimental Design towards Targeted Biomarker Discovery.Microarrays (Basel). 2015 Nov 3;4(4):520-39. doi: 10.3390/microarrays4040520. Microarrays (Basel). 2015. PMID: 27600238 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Combining Molecular, Imaging, and Clinical Data Analysis for Predicting Cancer Prognosis.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jun 30;14(13):3215. doi: 10.3390/cancers14133215. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35804988 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prostate cancer autoantibodies - applications in diagnosis, prognosis, monitoring disease progression and immunotherapy.Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2023 Apr 15;11(2):79-102. eCollection 2023. Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2023. PMID: 37168942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemical Proteomic Approaches Targeting Cancer Stem Cells: A Review of Current Literature.Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2017 Sep-Oct;14(5):315-327. doi: 10.21873/cgp.20042. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2017. PMID: 28870999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advancements in Electrochemical Biosensors for Alzheimer's Disease Biomarkers Detection.Curr Med Chem. 2021;28(20):4049-4073. doi: 10.2174/0929867327666201111141341. Curr Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33176635 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic analysis of circulating extracellular vesicles identifies potential markers of breast cancer progression, recurrence, and response.Sci Adv. 2020 Oct 2;6(40):eaba5714. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aba5714. Print 2020 Oct. Sci Adv. 2020. PMID: 33008904 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

