Localization of rem2 in the central nervous system of the adult rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss)
- PMID: 27600327
- PMCID: PMC5135629
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jchemneu.2016.09.001
Localization of rem2 in the central nervous system of the adult rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss)
Abstract
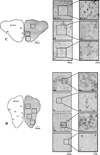
Rem2 is member of the RGK (Rem, Rad, and Gem/Kir) subfamily of the Ras superfamily of GTP binding proteins known to influence Ca2+ entry into the cell. In addition, Rem2, which is found at high levels in the vertebrate brain, is also implicated in cell proliferation and synapse formation. Though the specific, regional localization of Rem2 in the adult mammalian central nervous system has been well-described, such information is lacking in other vertebrates. Rem2 is involved in neuronal processes where the capacities between adults of different vertebrate classes vary. Thus, we sought to localize the rem2 gene in the central nervous system of an adult anamniotic vertebrate, the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). In situ hybridization using a digoxigenin (DIG)-labeled RNA probe was used to identify the regional distribution of rem2 expression throughout the trout central nervous system, while real-time polymerase chain reaction (rtPCR) further supported these findings. Based on in situ hybridization, the regional distribution of rem2 occurred within each major subdivision of the brain and included large populations of rem2 expressing cells in the dorsal telencephalon of the cerebrum, the internal cellular layer of the olfactory bulb, and the optic tectum of the midbrain. In contrast, no rem2 expressing cells were resolved within the cerebellum. These results were corroborated by rtPCR, where differential rem2 expression occurred between the major subdivisions assayed with the highest levels being found in the cerebrum, while it was nearly absent in the cerebellum. These data indicate that rem2 gene expression is broadly distributed and likely influences diverse functions in the adult fish central nervous system.
Keywords: Central nervous system; In situ hybridization; Rainbow trout.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Isolation and molecular characterization of Rem2 isoforms in the rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss): Tissue and central nervous system expression.Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2012 Feb;161(2):93-101. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2011.09.011. Epub 2011 Sep 29. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 21983188 Free PMC article.
-
Rem2 in the bullfrog (Rana catesbeiana): Patterns of expression within the central nervous system and brain expression at different ontogenetic stages.Gene. 2014 Apr 25;540(1):37-45. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2014.02.030. Epub 2014 Feb 24. Gene. 2014. PMID: 24576576 Free PMC article.
-
Rem2, a new member of the Rem/Rad/Gem/Kir family of Ras-related GTPases.Biochem J. 2000 Apr 1;347 Pt 1(Pt 1):223-31. Biochem J. 2000. PMID: 10727423 Free PMC article.
-
Short communication: Tissue-specific transcript expression of P-glycoprotein isoforms abcb1a and abcb1b in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) following induction with clotrimazole.Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2021 Feb-Mar;252:110538. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpb.2020.110538. Epub 2020 Nov 21. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33227421
-
New Approach for Untangling the Role of Uncommon Calcium-Binding Proteins in the Central Nervous System.Brain Sci. 2021 May 14;11(5):634. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11050634. Brain Sci. 2021. PMID: 34069107 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alvarado AS, Tsonis PA. Bridging the regeneration gap: genetic insights from diverse animal models. Nat Rev Genet. 2006;7:873–884. - PubMed
-
- Anglade I, Mazurais D, Douard V, Le Jossic-Corcos C, Mañanos EL, Michel D, Kah O. Distribution of glutamic acid decarboxylase mRNA in the forebrain of the rainbow trout as studied by in situ hybridization. J Comp Neurol. 1999;410(2):277–289. - PubMed
-
- Béguin P, Mahalakshmi RN, Nagashima K, Cher DH, Takahashi A, Yamada Y, Seino Y, Hunziker W. 14-3-3 and calmodulin control subcellular distribution of Kir/Gem and its regulation of cell shape and calcium channel activity. J Cell Sci. 2005;118:1923–1934. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

