Wnt4 is a novel biomarker for the early detection of kidney tubular injury after ischemia/reperfusion injury
- PMID: 27600466
- PMCID: PMC5013493
- DOI: 10.1038/srep32610
Wnt4 is a novel biomarker for the early detection of kidney tubular injury after ischemia/reperfusion injury
Abstract
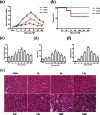
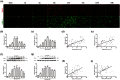
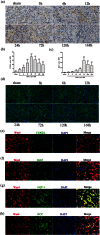
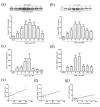
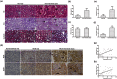
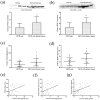
Earlier intervention after acute kidney injury would promote better outcomes. Our previous study found that Wnt proteins are promptly upregulated after ischemic kidney injury. Thus, we assessed whether Wnt4 could be an early and sensitive biomarker of tubular injury. We subjected mice to bilateral ischemia/reperfusion injury (IRI). Kidney and urinary Wnt4 expression showed an early increase at 3 hours and increased further at 24 hours post-IRI and was closely correlated with histopathological alterations. Serum creatinine slightly increased at 6 hours, indicating that it was less sensitive than Wnt4 expression. These data were further confirmed by clinical study. Both kidney and urinary Wnt4 expression were significantly increased in patients diagnosed with biopsy-proven minimal change disease (MCD) with tubular injury, all of whom nevertheless had normal estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) and serum creatinine. The increased Wnt4 expression also strongly correlated with histopathological alterations in these MCD patients. In conclusion, this is the first demonstration that increases in both kidney and urinary Wnt4 expression can be detected more sensitively and earlier than serum creatinine after kidney injury. In particular, urinary Wnt4 could be a potential noninvasive biomarker for the early detection of tubular injury.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Wnt4 is significantly upregulated during the early phases of cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury.Sci Rep. 2018 Jul 12;8(1):10555. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-28595-4. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30002385 Free PMC article.
-
Promotion of cell proliferation by clusterin in the renal tissue repair phase after ischemia-reperfusion injury.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014 Apr 1;306(7):F724-33. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00410.2013. Epub 2014 Jan 29. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24477687
-
Performance of Serum Creatinine and Kidney Injury Biomarkers for Diagnosing Histologic Acute Tubular Injury.Am J Kidney Dis. 2017 Dec;70(6):807-816. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2017.06.031. Epub 2017 Aug 24. Am J Kidney Dis. 2017. PMID: 28844586 Free PMC article.
-
Earlier recognition of nephrotoxicity using novel biomarkers of acute kidney injury.Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2011 Oct;49(8):720-8. doi: 10.3109/15563650.2011.615319. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2011. PMID: 21970770 Review.
-
DNA repair in ischemic acute kidney injury.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017 Apr 1;312(4):F551-F555. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00492.2016. Epub 2016 Dec 7. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27927651 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multiple Mechanisms are Involved in Salt-Sensitive Hypertension-Induced Renal Injury and Interstitial Fibrosis.Sci Rep. 2017 Apr 6;7:45952. doi: 10.1038/srep45952. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28383024 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive strategy for identifying extracellular vesicle surface proteins as biomarkers for chronic kidney disease.Front Physiol. 2024 Feb 6;15:1328362. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1328362. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38379702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pulsed ultrasound targeted to the spleen mitigates against kidney injury and promotes kidney repair.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2025 Aug 1;329(2):F234-F249. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00294.2024. Epub 2025 Jun 12. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40506227 Free PMC article.
-
Gray level co-occurrence matrix and wavelet analyses reveal discrete changes in proximal tubule cell nuclei after mild acute kidney injury.Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 10;13(1):4025. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-31205-7. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36899130 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt4 is significantly upregulated during the early phases of cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury.Sci Rep. 2018 Jul 12;8(1):10555. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-28595-4. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30002385 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pabla N. & Dong Z. et al.. Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: mechanisms and renoprotective strategies. Kidney Int. 73, 994–1007 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Ho J. et al.. Urinary, plasma, and serum biomarkers’ utility for predicting acute kidney injury associated with cardiac surgery in adults: a meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 66, 993–1005 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Sharfuddin A. A. & Molitoris B. A. Pathophysiology of ischemic acute kidney injury. Nat Rev Nephrol. 7, 189–200 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

