Post-mortem assessment in vascular dementia: advances and aspirations
- PMID: 27600683
- PMCID: PMC5011905
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-016-0676-5
Post-mortem assessment in vascular dementia: advances and aspirations
Abstract
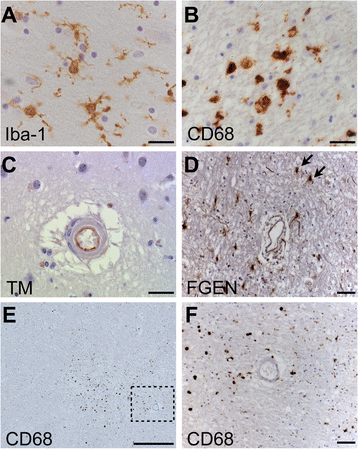
Background: Cerebrovascular lesions are a frequent finding in the elderly population. However, the impact of these lesions on cognitive performance, the prevalence of vascular dementia, and the pathophysiology behind characteristic in vivo imaging findings are subject to controversy. Moreover, there are no standardised criteria for the neuropathological assessment of cerebrovascular disease or its related lesions in human post-mortem brains, and conventional histological techniques may indeed be insufficient to fully reflect the consequences of cerebrovascular disease.
Discussion: Here, we review and discuss both the neuropathological and in vivo imaging characteristics of cerebrovascular disease, prevalence rates of vascular dementia, and clinico-pathological correlations. We also discuss the frequent comorbidity of cerebrovascular pathology and Alzheimer's disease pathology, as well as the difficult and controversial issue of clinically differentiating between Alzheimer's disease, vascular dementia and mixed Alzheimer's disease/vascular dementia. Finally, we consider additional novel approaches to complement and enhance current post-mortem assessment of cerebral human tissue.
Conclusion: Elucidation of the pathophysiology of cerebrovascular disease, clarification of characteristic findings of in vivo imaging and knowledge about the impact of combined pathologies are needed to improve the diagnostic accuracy of clinical diagnoses.
Keywords: Cerebrovascular disease; Cerebrovascular lesions; Magnetic resonance imaging; Mixed dementia; Neuropathology; Post-mortem MRI; Vascular cognitive impairment; Vascular dementia.
Figures




References
-
- Beach TG, Wilson JR, Sue LI, Newell A, Poston M, Cisneros R, Pandya Y, Esh C, Connor DJ, Sabbagh M, et al. Circle of Willis atherosclerosis: association with Alzheimer's disease, neuritic plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. Acta Neuropathol. 2007;113(1):13–21. doi: 10.1007/s00401-006-0136-y. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P50 AG023501/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G1100540/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 151/ALZS_/Alzheimer's Society/United Kingdom
- R01 AG040311/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G0800701/1/NC3RS_/National Centre for the Replacement, Refinement and Reduction of Animals in Research/United Kingdom
- G0400074/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0500247/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_14095/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0900652/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P01 AG019724/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G0502157/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

