Recent trends in burn epidemiology worldwide: A systematic review
- PMID: 27600982
- PMCID: PMC5616188
- DOI: 10.1016/j.burns.2016.08.013
Recent trends in burn epidemiology worldwide: A systematic review
Abstract
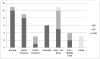
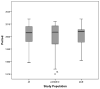
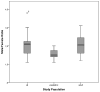
Burns have been more prevalent among low socioeconomic populations and in less developed regions. Incredible advances in burn care and social development over the recent decades, however, should have placed the incidence and severity of burns in a downwards trend. The aim of this review was to give an overview on current trends in burn epidemiology across the world. Also the socioeconomic development in countries that have published epidemiological data used in this study has been taken into account when comparing the results. There was a worldwide downwards trend of burn incidence, burn severity, length of hospital stay, and mortality rate. These findings were particularly pronounced in very highly developed countries. Data from highly and medium developed countries were more heterogeneous. No studies could be obtained from low and middle income countries. Comparisons between the different studies were compromised by the fact that studies emerged from specialized facilities on one hand and general hospitals on the other. Analyzed studies were also frequently focusing on limited patient populations such as "children" or "elderly". Our findings indicate the need for an international burn database with a minimal data-set in order to obtain objective and comparable results in respect of burn epidemiology.
Keywords: Burn; Development; Epidemiology; Mortality; Severity; Trend.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd and ISBI. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures

References
-
- Lentz CW, Potenza BM, Bernal N, Reigart CL, Faraklas I, Bessey PQ, et al. 2014 National Burn Repository, Report Data from 2004–2013. n.d
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

