Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Electrical and Optogenetic Deep Brain Stimulation at the Rat Nucleus Accumbens
- PMID: 27601003
- PMCID: PMC5013271
- DOI: 10.1038/srep31613
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Electrical and Optogenetic Deep Brain Stimulation at the Rat Nucleus Accumbens
Abstract
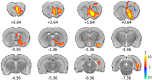
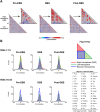
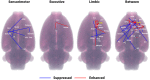
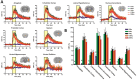
Deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens (NAc-DBS) is an emerging therapy for diverse, refractory neuropsychiatric diseases. Although DBS therapy is broadly hypothesized to work through large-scale neural modulation, little is known regarding the neural circuits and networks affected by NAc-DBS. Using a healthy, sedated rat model of NAc-DBS, we employed both evoked- and functional connectivity (fc) MRI to examine the functional circuit and network changes achieved by electrical NAc stimulation. Optogenetic-fMRI experiments were also undertaken to evaluate the circuit modulation profile achieved by selective stimulation of NAc neurons. NAc-DBS directly modulated neural activity within prefrontal cortex and a large number of subcortical limbic areas (e.g., amygdala, lateral hypothalamus), and influenced functional connectivity among sensorimotor, executive, and limbic networks. The pattern and extent of circuit modulation measured by evoked-fMRI was relatively insensitive to DBS frequency. Optogenetic stimulation of NAc cell bodies induced a positive fMRI signal in the NAc, but no other detectable downstream responses, indicating that therapeutic NAc-DBS might exert its effect through antidromic stimulation. Our study provides a comprehensive mapping of circuit and network-level neuromodulation by NAc-DBS, which should facilitate our developing understanding of its therapeutic mechanisms of action.
Figures


References
-
- Wichmann T. & Delong M. R. Deep brain stimulation for neurologic and neuropsychiatric disorders. Neuron 52, 197–204 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Goodman W. K. & Alterman R. L. Deep brain stimulation for intractable psychiatric disorders. Annu Rev Med 63, 511–524 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Floresco S. B. The nucleus accumbens: an interface between cognition, emotion, and action. Annu Rev Psychol 66, 25–52 (2015). - PubMed
-
- de Koning P. P., Figee M., van den Munckhof P., Schuurman P. R. & Denys D. Current status of deep brain stimulation for obsessive-compulsive disorder: a clinical review of different targets. Curr Psychiatry Rep 13, 274–282 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

