White sponge nevus: Report of three cases in a single family
- PMID: 27601826
- PMCID: PMC4989564
- DOI: 10.4103/0973-029X.185915
White sponge nevus: Report of three cases in a single family
Abstract
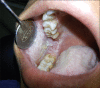
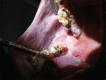
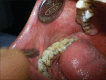
White sponge nevus (WSN) is an interesting hereditary oral mucosal disorder that commonly manifests as bilaterally symmetrical, thickened white, corrugated or velvety, diffuse plaques that predominantly affects the buccal mucosa. The lesions may develop at birth or later in childhood or adolescence. Because it is asymptomatic and benign, WSN requires no treatment. Recognition of this disorder is important due to its potential confusion with other lesions that may be found in the oral cavity. Emphasis should be given to the early and correct diagnosis of this disorder to avoid unnecessary treatment. This report presents three affected members of a single family.
Keywords: CK 13; CK 4; Cannon disease; genodermatosis; spongiosis; white plaque; white sponge nevus.
Figures




References
-
- Jorgenson RJ, Levin S. White sponge nevus. Arch Dermatol. 1981;117:73–6. - PubMed
-
- Regezi JA, Scuibba JJ, Jordan RC. Oral Pathology Clinical Pathologic Correlations. 6th ed. St. Louis: Saunders Elsevier; 2012. pp. 80–1.
-
- Hyde JN. An unusual naevus of the tongue in a five-year-old boy. J Cutan Dis. 1909;27:256.
-
- Cannon AB. White sponge nevus of the mucosa (nevus spongiosus albus mucosa) Arch Dermatol Syphilol. 1935;31:365–70.
-
- Rugg EL, McLean WH, Allison WE, Lunny DP, Macleod RI, Felix DH, et al. Amutation in the mucosal keratin K4 is associated with oral white sponge nevus. Nat Genet. 1995;11:450–2. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

