Users' Support as a Social Resource in Educational Services: Construct Validity and Measurement Invariance of the User-Initiated Support Scale (UISS)
- PMID: 27602008
- PMCID: PMC4993861
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2016.01248
Users' Support as a Social Resource in Educational Services: Construct Validity and Measurement Invariance of the User-Initiated Support Scale (UISS)
Abstract
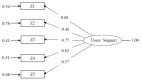
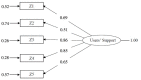
Social support is an important resource for reducing the risks of stress and burnout at work. It seems to be particularly helpful for educational and social professionals. The constant and intense relationships with users that characterize this kind of service can be very demanding, increasing stress and leading to burnout. While significant attention has been paid to supervisors and colleagues in the literature, users have rarely been considered as possible sources of social support. The only exception is the Zimmermann et al.'s (2011) research, focused on customer support as a resource for workers' well-being. This paper proposes the validation of the customer-initiated support scale developed by Zimmermann et al. (2011), translated into Italian and focused on educational services users (children's parents), to measure the user support perceived by workers: the User-Initiated Support Scale (UISS). In Study 1 (105 teachers), which specifically involved educators and kindergarten teachers, the items and scale properties were preliminarily examined using descriptive analyses and exploratory factor analysis (EFA). In Study 2 (304 teachers), the construct and criterion validity and scale dimensionality were analyzed using confirmatory factor analysis (CFA). In Study 3 (304 teachers from Study 2 and 296 educators), measurement invariance (MI) was tested. The EFA results from Study 1 showed a one-factor solution (explained variance, 67.2%). The scale showed good internal coherence (alpha = 0.88). The CFA in Study 2 validated the one-factor solution (comparative fit index = 0.987; standardized root mean square residual = 0.054). Bivariate correlations confirmed construct validity; the UISS was positively associated (convergent) with user gratitude, and not associated (divergent) with disproportionate customer expectations. Regarding the criterion validity test, the UISS was strongly correlated with burnout and job satisfaction. The analysis of MI performed on the Study 3 data confirmed the equality of the parameters of the covariance structure model between the two samples of kindergarten teachers and educators. This research study offers a useful version of a tool for measuring a crucial, but often ignored, protective resource for all professionals working directly with people (patients, students, and service users) that can represent important sources of well-being, directly or indirectly lessening the negative impacts of job demands.
Keywords: JD-R model; UISS; confirmatory factor analysis; educational services; measurement invariance; social resources; user support.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[French validation of the Verona Service Satisfaction Scale-VSSS-54F].Encephale. 2003 Mar-Apr;29(2):110-8. Encephale. 2003. PMID: 14567162 French.
-
Collective Empowerment in Online Health Communities: Scale Development and Empirical Validation.J Med Internet Res. 2019 Nov 20;21(11):e14392. doi: 10.2196/14392. J Med Internet Res. 2019. PMID: 31746772 Free PMC article.
-
The Chinese version of the Perceived Stress Questionnaire: development and validation amongst medical students and workers.Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2020 Mar 13;18(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s12955-020-01307-1. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2020. PMID: 32169070 Free PMC article.
-
Measuring Electronic Health Literacy: Development, Validation, and Test of Measurement Invariance of a Revised German Version of the eHealth Literacy Scale.J Med Internet Res. 2022 Feb 2;24(2):e28252. doi: 10.2196/28252. J Med Internet Res. 2022. PMID: 35107437 Free PMC article.
-
Development, validation and psychometric evaluation of the Chinese version of the biopsychosocial impact scale in orofacial pain patients.Front Psychol. 2023 Mar 7;14:1101383. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1101383. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 36960011 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Sometimes It Drains, Sometimes It Sustains: The Dual Role of the Relationship with Students for University Professors.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Jul 16;2019:9875090. doi: 10.1155/2019/9875090. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31380445 Free PMC article.
-
A New Academic Quality at Work Tool (AQ@workT) to Assess the Quality of Life at Work in the Italian Academic Context.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Mar 21;19(6):3724. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19063724. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35329409 Free PMC article.
-
First validation of the technical and administrative staff quality of life at work tool (TASQ@work) in academia.Front Psychol. 2024 Apr 12;15:1346556. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1346556. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38680287 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Avallone F., Paplomatas A. (2005). Salute Organizzativa, Psicologia Del Benessere Nei Contesti Lavorativi. Milano: Raffaello Cortina Editore.
-
- Bakker A. B., Demerouti E., Schaufeli W. B. (2003). Dual processes at work in a call centre: an application of the job demands a resources model. Eur. J. Work Organ. Psychol. 12 393–417. 10.1080/13594320344000165 - DOI
-
- Bakker A. B., Hakanen J. J., Demerouti E., Xanthopoulou D. (2007). Job resources boost work engagement, particularly when job demands are high. J. Educ. Psychol. 99 274–284. 10.1037/0022-0663.99.2.274 - DOI
-
- Bentler P. M. (1995). EQS Structural Equations Program Manual. Encino, CA: Multivariate Software.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous