Effects of phased joint intervention on Rho/ROCK expression levels in patients with portal hypertension
- PMID: 27602079
- PMCID: PMC4998197
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2016.3454
Effects of phased joint intervention on Rho/ROCK expression levels in patients with portal hypertension
Abstract
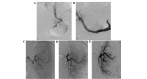
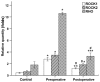
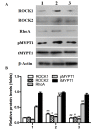
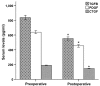
The current study investigated the effects of phased joint intervention on clinical efficacy and Rho/Rho-associated coil protein kinase (ROCK) expression in patients with portal hypertension complicated by esophageal variceal bleeding (EVB) and hypersplenism. Patients with portal hypertension (n=53) caused by liver cirrhosis complicated by EVB and hypersplenism treated with phased joint intervention were assessed, and portal hemodynamics, blood, liver function, complications, and rebleeding incidence were analyzed. Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction was used to measure Rho, ROCK1 and ROCK2 mRNA expression levels in peripheral blood mononuclear cells prior to and following phased joint intervention, and western blotting was employed to determine the protein expression levels of Rho, ROCK1, ROCK2, phosphorylated (p) myosin phosphatase target subunit 1 (MYPT1) and total-MYPT1. All patients underwent an emergency assessment of hemostasis with a 100% success rate. Varicose veins were alleviated, and portal hemodynamics and liver function improved following intervention. Furthermore, preoperative and postoperative expression levels of Rho, ROCK1 and ROCK2 mRNA were higher compared with the control group. Notably, the mRNA expression levels of Rho, ROCK1 and ROCK2 in the postoperative group were significantly lower when compared with the preoperative group. Protein expression levels of Rho, ROCK1, ROCK2 and pMYPT1 in the postoperative group were lower, as compared with the preoperative group. Concentration levels of transforming growth factor-β1, connective tissue growth factor and platelet-derived growth factor in peripheral blood were significantly reduced following phased joint intervention. Therefore, the present findings demonstrated that phased joint intervention is able to effectively treat EVB and hypersplenism, and improve liver function. The efficacy of phased joint intervention may be associated with its role in the regulation of the Rho-ROCK signaling pathway.
Keywords: Rho; cirrhosis; embolization; esophageal varices; rock.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of phased joint intervention on IL-35 and IL-17 expression levels in patients with portal hypertension.Int J Mol Med. 2014 May;33(5):1131-9. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2014.1662. Epub 2014 Feb 19. Int J Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24549402
-
[Role of Rho/ROCK signaling pathway in the protective effects of hydrogen against acute lung injury in septic mice].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2016 May;28(5):401-6. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2016. PMID: 29920028 Chinese.
-
Disruption of both ROCK1 and ROCK2 genes in cardiomyocytes promotes autophagy and reduces cardiac fibrosis during aging.FASEB J. 2019 Jun;33(6):7348-7362. doi: 10.1096/fj.201802510R. Epub 2019 Mar 8. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 30848941 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Ras Homolog C/Rho-Associated Coiled-Protein Kinase (Rho/ROCK) Signaling Pathways on Proliferation and Apoptosis of Human Myeloma Cells.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Oct 10;25:7605-7616. doi: 10.12659/MSM.915998. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 31599230 Free PMC article.
-
The Physiology, Pathology, and Therapeutic Interventions for ROCK Isoforms in Diabetic Kidney Disease.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Sep 25;11:585633. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.585633. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33101039 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
