Regulatory effect of cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant, epithelial neutrophil-activating peptide 78 and pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate on pulmonary neutrophil aggregation mediated by nuclear factor-κB in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome mice
- PMID: 27602092
- PMCID: PMC4998193
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2016.3520
Regulatory effect of cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant, epithelial neutrophil-activating peptide 78 and pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate on pulmonary neutrophil aggregation mediated by nuclear factor-κB in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome mice
Abstract
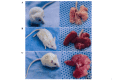
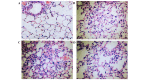
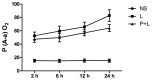
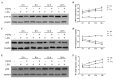
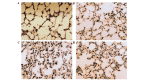
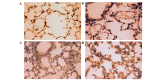
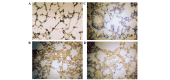
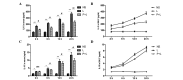
In the present study, the regulatory effect of cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant (CINC) and epithelial neutrophil-activating peptide 78 (ENA-78) on pulmonary neutrophil (PMN) accumulation in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) mice, and the therapeutic effect of pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC), was investigated. BALB/c mice were divided into control, LPS and PDTC + LPS groups using a random number table. The phosphorylation of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) was detected using a western blot, and the mRNA expression levels of CINC were evaluated using reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction. The expression of NF-κB, CINC and ENA-78 was detected using immunohistochemistry. The production of interleukin (IL)-8 and IL-10 in serum and broncho-alveolar lavage fluid (BALF) was analyzed using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The total number of leukocytes and proportion of PMNs in BALF was also determined. Following injection with LPS (20 mg/kg), the expression levels of p-NF-κB, CINC and ENA-78 were increased in lung tissue, and the expression levels of IL-8, IL-10 and the number of PMNs increased in serum and BALF. However, in comparison with the LPS group, the degree of lung injury was reduced in ARDS mice that were treated with PDTC. In addition, the expression level of p-NF-κB and the production of chemokines in lung tissue decreased in ARDS mice that were treated with PDTC, and the number of PMNs in BALF also decreased. In conclusion, the results of the present study suggest that the LPS-induced phosphorylation of NF-κB may result in the synthesis and release of CINC and ENA-78, which induce the accumulation of PMNs in the lung. Therefore, PDTC may be used to reduce the production of chemokines and cytokines, thereby decreasing the activation of PMNs in lung tissue and reducing the damage of lung tissue in ARDS.
Keywords: acute respiratory distress syndrome; cytokine-induced neutrophil chemoattractant; epithelial neutrophil-activating peptide 78; nuclear factor-κB; polymorphonuclear neutrophils.
Figures

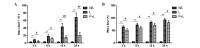
Similar articles
-
Regulatory mechanism of pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate is mediated by nuclear factor-κB and inhibits neutrophil accumulation in ARDS mice.Exp Ther Med. 2014 Aug;8(2):614-622. doi: 10.3892/etm.2014.1738. Epub 2014 May 28. Exp Ther Med. 2014. PMID: 25009629 Free PMC article.
-
Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate attenuates endotoxin-induced acute lung injury.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1997 Nov;17(5):608-16. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.17.5.2661. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1997. PMID: 9374112
-
Schisantherin A protects lipopolysaccharide-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome in mice through inhibiting NF-κB and MAPKs signaling pathways.Int Immunopharmacol. 2014 Sep;22(1):133-40. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2014.06.004. Epub 2014 Jun 27. Int Immunopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24975658
-
Nanomedicine for acute respiratory distress syndrome: The latest application, targeting strategy, and rational design.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021 Oct;11(10):3060-3091. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.04.023. Epub 2021 May 7. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021. PMID: 33977080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The mercurial nature of neutrophils: still an enigma in ARDS?Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2014 Feb;306(3):L217-30. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00311.2013. Epub 2013 Dec 6. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24318116 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protective effects of the suppressed NF-κB/TLR4 signaling pathway on oxidative stress of lung tissue in rat with acute lung injury.Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2019 May;35(5):265-276. doi: 10.1002/kjm2.12065. Epub 2019 Apr 18. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31001923 Free PMC article.
-
Nalbuphine alleviates inflammation by down-regulating NF-κB in an acute inflammatory visceral pain rat model.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2022 Jun 1;23(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s40360-022-00573-7. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35642022 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of 2-methoxycinnamaldehyde an active ingredients of Cinnamomum cassia on warm hepatic ischemia reperfusion injury in rat model.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2019 Dec;22(12):1400-1407. doi: 10.22038/IJBMS.2019.13987. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 32133057 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
