Augmented expression of Polo-like kinase 1 is a strong predictor of shorter cancer-specific overall survival in early stage breast cancer at 15-year follow-up
- PMID: 27602103
- PMCID: PMC4998224
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2016.4890
Augmented expression of Polo-like kinase 1 is a strong predictor of shorter cancer-specific overall survival in early stage breast cancer at 15-year follow-up
Abstract
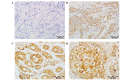
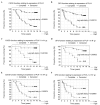
Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) is a serine-threonine kinase that plays a crucial role in the regulation of cell division. In addition, it acts as a modulator of the DNA damage response and as a novel factor in the maintenance of genome stability during DNA replication. The present study aimed to reveal the associations between PLK1 expression and clinicopathological features of patients with breast cancer (BC), particularly patient survival at 5-, 10- and 15-year follow-up. PLK1 expression was evaluated immunohistochemically in routine diagnostic tissue specimens from 83 patients treated radically for stage II BC. Kaplan-Meier analysis revealed a correlation between PLK1 overexpression and long-term survival. High PLK1 immunoreactivity was associated with shorter cancer-specific overall survival (CSOS) and disease-free survival (P=0.00001 and 0.00013, respectively). Multivariate analysis confirmed the negative prognostic significance of PLK1 overexpression for CSOS in all 83 patients (P=0.00030). Furthermore, analogous correlations were observed in both subgroups with and without nodal metastases (P=0.01400 and 0.01200, respectively). The present results indicate that PLK1 expression has a prognostic role in early BC. Immunohistochemical assessment of PLK1 reactivity may potentially become a qualifier for inclusion of PLK1 inhibitor therapy.
Keywords: Polo-like kinase 1; breast cancer; prognosis; survival analysis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characteristics and prognostic significance of polo-like kinase-1 (PLK1) expression in breast cancer.Histopathology. 2023 Sep;83(3):414-425. doi: 10.1111/his.14960. Epub 2023 May 24. Histopathology. 2023. PMID: 37222669
-
Augmented expression of polo-like kinase 1 indicates poor clinical outcome for breast patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Oncotarget. 2017 Apr 20;8(34):57723-57732. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17301. eCollection 2017 Aug 22. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28915707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Misregulation of polo-like protein kinase 1, P53 and P21WAF1 in epithelial ovarian cancer suggests poor prognosis.Oncol Rep. 2015 Mar;33(3):1235-42. doi: 10.3892/or.2015.3723. Epub 2015 Jan 15. Oncol Rep. 2015. PMID: 25592872
-
Clinicopathological and prognostic implications of polo-like kinase 1 expression in colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Gene. 2019 Dec 30;721:144097. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.144097. Epub 2019 Sep 4. Gene. 2019. PMID: 31493507
-
Decreased PLK1 expression denotes therapy resistance and unfavourable disease-free survival in rectal cancer patients receiving neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy.Pathol Res Pract. 2016 Dec;212(12):1133-1137. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2016.09.012. Epub 2016 Sep 22. Pathol Res Pract. 2016. PMID: 27712975
Cited by
-
CEBP-β and PLK1 as Potential Mediators of the Breast Cancer/Obesity Crosstalk: In Vitro and In Silico Analyses.Nutrients. 2023 Jun 22;15(13):2839. doi: 10.3390/nu15132839. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37447165 Free PMC article.
-
LFM-A13, a potent inhibitor of polo-like kinase, inhibits breast carcinogenesis by suppressing proliferation activity and inducing apoptosis in breast tumors of mice.Invest New Drugs. 2018 Jun;36(3):388-395. doi: 10.1007/s10637-017-0540-2. Epub 2017 Nov 15. Invest New Drugs. 2018. PMID: 29139009
-
Identifying M1-like macrophage related genes for prognosis prediction in lung adenocarcinoma based on a gene co-expression network.Heliyon. 2023 Jan 4;9(1):e12798. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e12798. eCollection 2023 Jan. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 36711278 Free PMC article.
-
DNA polymerase β deficiency promotes the occurrence of esophageal precancerous lesions in mice.Neoplasia. 2021 Jul;23(7):663-675. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2021.05.001. Epub 2021 Jun 15. Neoplasia. 2021. PMID: 34144266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harnessing the value of TCTP in breast cancer treatment resistance: an opportunity for personalized therapy.Cancer Drug Resist. 2023 Jul 13;6(3):447-467. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2023.21. eCollection 2023. Cancer Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 37842235 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- de Cárcer G, Escobar B, Higuero AM, García L, Ansón A, Pérez G, Mollejo M, Manning G, Meléndez B, Abad-Rodríguez J, Malumbres M. Plk5, a polo box domain-only protein with specific roles in neuron differentiation and glioblastoma suppression. Mol Cell Biol. 2011;31:1225–1239. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00607-10. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
