Influence of autologous dendritic cells on cytokine-induced killer cell proliferation, cell phenotype and antitumor activity in vitro
- PMID: 27602134
- PMCID: PMC4998518
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2016.4839
Influence of autologous dendritic cells on cytokine-induced killer cell proliferation, cell phenotype and antitumor activity in vitro
Abstract
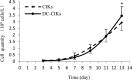
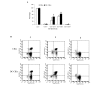
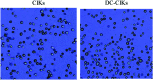
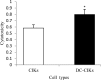
Dendritic cell (DCs) are essential antigen processing and presentation cells that play a key role in the immune response. In this study, DCs were co-cultured with cytokine-induced killer cells (DC-CIKs) in vitro to detect changes in cell proliferation, cell phenotype and cell cytotoxicity. The results revealed that the DCs were suitable for co-culture with CIKs at day 7, and that cell quantity of DC-CIKs was lower than that of CIKs until day 11, but it was significantly improved to 1.17-fold that of CIKs at day 13. Flow cytometry was used to detect the cell phenotype of CIKs and DC-CIKs. Compared with CIKs at day 13, the percentage of CD3+, CD3+CD4+, CD3+CD8+ and CD3+CD56+ T cells in DC-CIKs was significantly improved 1.02, 1.79, 1.26 and 2.44-fold, respectively. In addition, trypan blue staining analysis demonstrated that the cell viability of CIKs and DC-CIKs was 96% and 98%, respectively. Furthermore, 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) analysis verified that CIK and DC-CIK cytotoxicity in Hela cells was 58% and 80%, respectively, with a significant difference. Taken together, our results indicate that the cell proliferation, cell phenotype and antitumor activity of CIKs were all enhanced following co-culture with DCs in vitro. These results are likely to be useful for DC-CIK application in antitumor therapies.
Keywords: MTT; cytokine-induced killer cells; dendritic cells; flow cytometry.
Figures

References
-
- Wongkajornsilp A, Wamanuttajinda V, Kasetsinsombat K, Duangsa-ard S, Sa-ngiamsuntorn K, Hongeng S, Maneechotesuwan K. Sunitinib indirectly enhanced anti-tumor cytotoxicity of cytokine-induced killer cells and CD3+CD56+ subset through the co-culturing dendritic cells. PLoS One. 2013;8:e78980. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078980. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
