Enhancing chemosensitivity in oral squamous cell carcinoma by lentivirus vector-mediated RNA interference targeting EGFR and MRP2
- PMID: 27602148
- PMCID: PMC4998589
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2016.4883
Enhancing chemosensitivity in oral squamous cell carcinoma by lentivirus vector-mediated RNA interference targeting EGFR and MRP2
Abstract
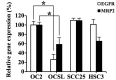
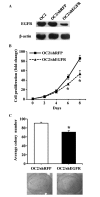
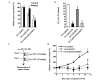
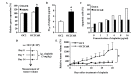
Oral cancer is the eighth most common type of cancer among men worldwide, with an age-standardized rate of 6.3 per 100,000, and is the fourth leading cause of cancer-associated mortality among men in Taiwan. Cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) are two of the most frequently utilized chemotherapy drugs for the treatment of oral cancer. Although oral cancer patients initially benefit from chemotherapy with these drugs, they may develop resistance to them, which worsens their prognosis and reduces survival rates. It has been reported that increased levels of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 (MRP2) induce drug resistance in numerous types of human cancer. Therefore, the present study employed lentivirus vector-mediated RNA interference (RNAi) in order to target the genes encoding EGFR and MRP2 in the oral squamous cell carcinoma cell line OC2. It was observed that RNAi-mediated downregulation of EGFR or MRP2 increased the sensitivity to 5-FU and cisplatin in OC2 cells. Downregulation of EGFR resulted in significant suppression of OC2 tumor growth following 5-FU administration. However, simultaneous downregulation of the two genes did not further suppress the tumor growth, indicating that MRP2 does not have a significant role in the chemosensitivity of EGFR-downregulated cells to 5-FU. In contrast, downregulation of MRP2 was demonstrated to significantly enhance the therapeutic effects of cisplatin in EGFR-downregulated OC2 tumors. The observation that the expression of MRP2 was positively correlated with the level of cisplatin resistance in cells suggests that RNAi-mediated downregulation of MRP2 may be applicable as a therapeutic approach toward reversing MRP2-dependent cisplatin resistance in oral cancer.
Keywords: RNA interference; chemosensitivity; epidermal growth factor receptor; multidrug resistance-associated protein 2; oral cancer.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lentivirus-mediated shRNA targeting of cyclin D1 enhances the chemosensitivity of human gastric cancer to 5-fluorouracil.Int J Oncol. 2013 Dec;43(6):2007-14. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2013.2119. Epub 2013 Oct 3. Int J Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24100731
-
[Double sites short hairpin RNAs targeting epidermal growth factor receptor to promote colon cancer cells apoptosis and enhance 5-fluorouracil chemotherapy effect].Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2006 Jun 1;44(11):765-9. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 16836928 Chinese.
-
The monoclonal antibody CH12 augments 5-fluorouracil-induced growth suppression of hepatocellular carcinoma xenografts expressing epidermal growth factor receptor variant III.Cancer Lett. 2014 Jan 1;342(1):113-20. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.08.038. Epub 2013 Sep 2. Cancer Lett. 2014. PMID: 24007863
-
Lentivirus-mediated RNAi silencing targeting ABCC2 increasing the sensitivity of a human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line against cisplatin.J Transl Med. 2008 Oct 4;6:55. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-6-55. J Transl Med. 2008. PMID: 18834541 Free PMC article.
-
Cetuximab: an epidermal growth factor receptor chemeric human-murine monoclonal antibody.Drugs Today (Barc). 2005 Feb;41(2):107-27. doi: 10.1358/dot.2005.41.2.882662. Drugs Today (Barc). 2005. PMID: 15821783 Review.
Cited by
-
HNCDrugResDb: a platform for deciphering drug resistance in head and neck cancers.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 25;14(1):25327. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-75861-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39455682 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Natural Autoantibodies to HER2-Derived Peptides Performed Antitumor Effects on Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 5;12:693989. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.693989. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34803666 Free PMC article.
-
Role Played by Paraoxonase-2 Enzyme in Cell Viability, Proliferation and Sensitivity to Chemotherapy of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 25;24(1):338. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010338. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613780 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic downregulation of the proapoptotic gene HOXA5 in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Mol Med Rep. 2025 Mar;31(3):56. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13421. Epub 2024 Dec 20. Mol Med Rep. 2025. PMID: 39704209 Free PMC article.
-
The role of non-coding RNAs in drug resistance of oral squamous cell carcinoma and therapeutic potential.Cancer Commun (Lond). 2021 Oct;41(10):981-1006. doi: 10.1002/cac2.12194. Epub 2021 Jul 20. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2021. PMID: 34289530 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- de Camargo Cancela M, Voti L, Guerra-Yi M, Chapuis F, Mazuir M, Curado MP. Oral cavity cancer in developed and in developing countries: Population-based incidence. Head Neck. 2010;32:357–367. - PubMed
-
- 2009 Statistics of Causes of Death. Ministry of Health and Welfare; Taipei, Taiwan: 2010.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
