Aloe-emodin suppresses esophageal cancer cell TE1 proliferation by inhibiting AKT and ERK phosphorylation
- PMID: 27602169
- PMCID: PMC4998577
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2016.4910
Aloe-emodin suppresses esophageal cancer cell TE1 proliferation by inhibiting AKT and ERK phosphorylation
Abstract
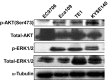
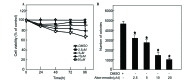
Aberrant AKT and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) activation is often observed in various human cancers. Both AKT and ERK are important in the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase/ERK signaling pathways, which play vital roles in cell proliferation, differentiation and survival. Compounds that are able to block these pathways have therefore a promising use in cancer treatment and prevention. The present study revealed that AKT and ERK are activated in esophageal cancer TE1 cells. Aloe-emodin, an anthraquinone present in aloe latex, can suppress TE1 cell proliferation and anchor-independent cell growth. Aloe-emodin can also reduce the number of TE1 cells in S phase. Protein analysis indicated that aloe-emodin inhibits the phosphorylation of AKT and ERK in a dose-dependent manner. Overall, the present data indicate that aloe-emodin can suppress TE1 cell growth by inhibiting AKT and ERK phosphorylation, and suggest its clinical use for cancer therapy.
Keywords: aloe-emodin; esophageal cancer; signal transduction pathway.
Figures



References
-
- Ghasemi-Kebria F, Roshandel G, Semnani S, Shakeri R, Khoshnia M, Naeimi-Tabiei M, Merat S, Malekzadeh R. Marked increase in the incidence rate of esophageal adenocarcinoma in a high-risk area for esophageal cancer. Arch Iran Med. 2013;16:320–323. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
