Anti-VP6 VHH: An Experimental Treatment for Rotavirus A-Associated Disease
- PMID: 27603013
- PMCID: PMC5014449
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162351
Anti-VP6 VHH: An Experimental Treatment for Rotavirus A-Associated Disease
Abstract
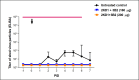
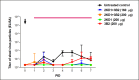
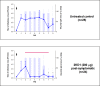
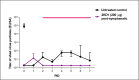
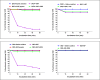
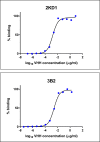
Species A Rotaviruses (RVA) remain a leading cause of mortality in children under 5 years of age. Current treatment options are limited. We assessed the efficacy of two VP6-specific llama-derived heavy chain antibody fragments (VHH) -2KD1 and 3B2- as an oral prophylactic and therapeutic treatment against RVA-induced diarrhea in a neonatal mouse model inoculated with virulent murine RVA (ECw, G16P[16]I7). Joint therapeutic administration of 2KD1+3B2 (200 μg/dose) successfully reduced diarrhea duration, RVA infection severity and virus shedding in feces. While the same dose of 2KD1 or 3B2 (200 μg) significantly reduced duration of RVA-induced diarrhea, 2KD1 was more effective in diminishing the severity of intestinal infection and RVA shedding in feces, perhaps because 2KD1 presented higher binding affinity for RVA particles than 3B2. Neither prophylactic nor therapeutic administration of the VHH interfered with the host's humoral immune response against RVA. When 2KD1 (200 μg) was administered after diarrhea development, it also significantly reduced RVA intestinal infection and fecal shedding. Host antibody responses against the oral VHH treatment were not detected, nor did viral escape mutants. Our findings show that oral administration of anti-VP6 VHH constitute, not only an effective prophylactic treatment against RVA-associated diarrhea, but also a safe therapeutic tool against RVA infection, even once diarrhea is present. Anti-VP6 VHH could be used complementary to ongoing vaccination, especially in populations that have shown lower immunization efficacy. These VHH could also be scaled-up to develop pediatric medication or functional food like infant milk formulas that might help treat RVA diarrhea.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Recombinant monovalent llama-derived antibody fragments (VHH) to rotavirus VP6 protect neonatal gnotobiotic piglets against human rotavirus-induced diarrhea.PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(5):e1003334. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003334. Epub 2013 May 2. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23658521 Free PMC article.
-
Controlling Rotavirus-associated diarrhea: Could single-domain antibody fragments make the difference?Rev Argent Microbiol. 2015 Oct-Dec;47(4):368-79. doi: 10.1016/j.ram.2015.09.005. Epub 2015 Dec 1. Rev Argent Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26654700
-
Lactobacilli expressing variable domain of llama heavy-chain antibody fragments (lactobodies) confer protection against rotavirus-induced diarrhea.J Infect Dis. 2006 Dec 1;194(11):1580-8. doi: 10.1086/508747. Epub 2006 Oct 23. J Infect Dis. 2006. PMID: 17083044
-
Porcine group A rotaviruses with heterogeneous VP7 and VP4 genotype combinations can be found together with enteric bacteria on Belgian swine farms.Vet Microbiol. 2014 Aug 6;172(1-2):23-34. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2014.04.002. Epub 2014 Apr 13. Vet Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24837191 Review.
-
[Rotaviruses in human and veterinary medicine].Sante. 1997 May-Jun;7(3):195-9. Sante. 1997. PMID: 9296811 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Nanobodies: Prospects of Expanding the Gamut of Neutralizing Antibodies Against the Novel Coronavirus, SARS-CoV-2.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 23;11:1531. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01531. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32655584 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Single-Domain Antibodies As Therapeutics against Human Viral Diseases.Front Immunol. 2017 Dec 13;8:1802. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01802. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29326699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single domain antibodies from camelids in the treatment of microbial infections.Front Immunol. 2024 May 17;15:1334829. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1334829. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38827746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correlates of immune protection against human rotaviruses: natural infection and vaccination.Arch Virol. 2024 Mar 8;169(3):72. doi: 10.1007/s00705-024-05975-y. Arch Virol. 2024. PMID: 38459213 Review.
-
Fit-for-purpose heterodivalent single-domain antibody for gastrointestinal targeting of toxin B from Clostridium difficile.Protein Sci. 2024 Jul;33(7):e5035. doi: 10.1002/pro.5035. Protein Sci. 2024. PMID: 38923049 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO- UNICEF, Johns Hopkins School of Public Health U. Implementing the New Recommendations on the Clinical Management of Diarrhoea Guidelines for Policy Makers and Programme Managers. World Health Organization, Department of Child and Adolescent Health and Development, and United Nations Children’s Fund, Programme Division; 2006.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

