Transcriptomic Profiling Analysis of Arabidopsis thaliana Treated with Exogenous Myo-Inositol
- PMID: 27603208
- PMCID: PMC5014391
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161949
Transcriptomic Profiling Analysis of Arabidopsis thaliana Treated with Exogenous Myo-Inositol
Abstract
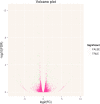
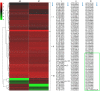
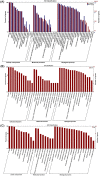
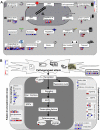
Myo-insositol (MI) is a crucial substance in the growth and developmental processes in plants. It is commonly added to the culture medium to promote adventitious shoot development. In our previous work, MI was found in influencing Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. In this report, a high-throughput RNA sequencing technique (RNA-Seq) was used to investigate differently expressed genes in one-month-old Arabidopsis seedling grown on MI free or MI supplemented culture medium. The results showed that 21,288 and 21,299 genes were detected with and without MI treatment, respectively. The detected genes included 184 new genes that were not annotated in the Arabidopsis thaliana reference genome. Additionally, 183 differentially expressed genes were identified (DEGs, FDR ≤0.05, log2 FC≥1), including 93 up-regulated genes and 90 down-regulated genes. The DEGs were involved in multiple pathways, such as cell wall biosynthesis, biotic and abiotic stress response, chromosome modification, and substrate transportation. Some significantly differently expressed genes provided us with valuable information for exploring the functions of exogenous MI. RNA-Seq results showed that exogenous MI could alter gene expression and signaling transduction in plant cells. These results provided a systematic understanding of the functions of exogenous MI in detail and provided a foundation for future studies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Boss WF, Davis AJ, Im YJ, Galvão RM, Perera IY. Phosphoinositide metabolism: towards an understanding of subcellular signaling. Subcell Biochem. 2006; 39: 181–205. - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium oscillations. Biochem Soc Symp. 2007; 74: 1–7. - PubMed
-
- Loewus F. Structure and occurrence of inositols in plants In: Morre D J, Boss WF, Loewus FA, editors. Inositol Metabolism in Plants. Wiley-Liss Inc; New York, 1990. pp. 1–11.
-
- Loewus FA, Murthy P. Myo-inositol metabolism in plants. Plant Sci. 2000; 150: 1–19.
-
- Murashige T, Skoog F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue culture. Physiol Plant. 1962; 15: 473–497.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

