From Wet-Lab to Variations: Concordance and Speed of Bioinformatics Pipelines for Whole Genome and Whole Exome Sequencing
- PMID: 27604516
- PMCID: PMC5129537
- DOI: 10.1002/humu.23114
From Wet-Lab to Variations: Concordance and Speed of Bioinformatics Pipelines for Whole Genome and Whole Exome Sequencing
Abstract
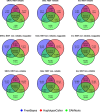
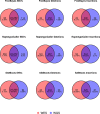
As whole genome sequencing becomes cheaper and faster, it will progressively substitute targeted next-generation sequencing as standard practice in research and diagnostics. However, computing cost-performance ratio is not advancing at an equivalent rate. Therefore, it is essential to evaluate the robustness of the variant detection process taking into account the computing resources required. We have benchmarked six combinations of state-of-the-art read aligners (BWA-MEM and GEM3) and variant callers (FreeBayes, GATK HaplotypeCaller, SAMtools) on whole genome and whole exome sequencing data from the NA12878 human sample. Results have been compared between them and against the NIST Genome in a Bottle (GIAB) variants reference dataset. We report differences in speed of up to 20 times in some steps of the process and have observed that SNV, and to a lesser extent InDel, detection is highly consistent in 70% of the genome. SNV, and especially InDel, detection is less reliable in 20% of the genome, and almost unfeasible in the remaining 10%. These findings will aid in choosing the appropriate tools bearing in mind objectives, workload, and computing infrastructure available.
Keywords: NA12878; NGS; alignment; benchmark; bioinformatics; computing speed; variant calling; whole exome sequencing; whole genome sequencing.
© 2016 The Authors. **Human Mutation published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Biesecker LG, Green RC. 2014. Diagnostic clinical genome and exome sequencing. N Engl J Med 370:2418–2425. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

