Dietary Guidelines for Chinese Residents (2016): comments and comparisons
- PMID: 27604857
- PMCID: PMC5018612
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.B1600341
Dietary Guidelines for Chinese Residents (2016): comments and comparisons
Abstract
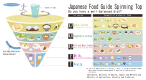
A high quality diet is believed to play a functional role in promoting the healthy growth of mankind and preventing many kinds of chronic degenerative diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and obesity. Adherence to a high quality diet has been strongly associated with a lower risk of mortality. To help promote healthy lifestyles and physical strength, the Chinese government has produced a new revised version of the Dietary Guidelines for Chinese Residents (2016) and the Chinese Food Pagoda, as guidance for dietary intake among its population. Similarly, the Japanese government has produced the Japanese Food Guide Spinning Top Model, and the US government has recently published revised dietary recommendations in its 2015-2020 eighth edition of Dietary Guidelines for Americans. The evidence from all respective cohort studies involved in producing these guidelines shows a reduced risk of many chronic diseases and mortality if the guidelines are followed. All scientific findings support encouraging the general population to consume a broad variety of food on the basis of nutrient and food intakes in order to prevent deficiency diseases and a surplus of energy and nutrients, and recommend daily physical activity for health promotion.
Keywords: Chinese Food Pagoda; Dietary Guidelines for Americans; Dietary guidelines; Japanese Food Guide Spinning Top.
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with ethics guidelines: Shan-shan WANG, Sovichea LAY, Hai-ning YU, and Sheng-rong SHEN declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Figures



References
-
- The Chinese Nutrition Society. Dietary Guidelines and the Food Guide Pagoda. J Am Diet Assoc. 2000;100(8):886–887. (Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0002-8223(00)00257-1) - DOI - PubMed
-
- The Chinese Nutrition Society. The Food Guide Pagoda for Chinese Residents. Available from http://dg.cnsoc.org/upload/images/source/20160519163856103.jpg [Accessed on June 20, 2016]; 2016. (in Chinese)
-
- Kurotani K, Akter S, Kashino I, et al. Quality of diet and mortality among Japanese men and women: Japan Public Health Center based prospective study. . BMJ. 2016;352:i1209. (Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.i1209) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare and the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries of Japan. Japanese Food Guide Spinning Top. Available from http://www.maff.go.jp/j/balance_guide/b_use/pdf/eng_reiari. pdf [Accessed on June 30, 2016].2005.
-
- National Health and Medical Research Council. Dietary Guidelines for Australians. Canberra: Australian Government Publishing; 1992.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

