Protective effects of parecoxib on rat primary astrocytes from oxidative stress induced by hydrogen peroxide
- PMID: 27604861
- PMCID: PMC5018616
- DOI: 10.1631/jzus.B1600017
Protective effects of parecoxib on rat primary astrocytes from oxidative stress induced by hydrogen peroxide
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the protective effects of parecoxib from oxidative stress induced by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in rat astrocytes in vitro.
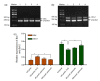
Methods: All experiments included 4 groups: (1) negative control (NC) group, without any treatment; (2) H2O2 treatment group, 100 μmol/L H2O2 treatment for 24 h; (3) and (4) parecoxib pretreatment groups, 80 and 160 μmol/L parecoxib treatment for 24 h, respectively, and then treated with 100 μmol/L H2O2. Several indices were investigated, and the expressions of Bax, Bcl-2, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) were quantified.
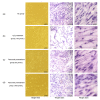
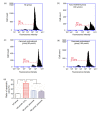
Results: Compared to the NC group, exposure to H2O2 resulted in significant morphological changes, which could be reversed by pretreatment of parecoxib. In addition, H2O2 treatment led to loss of viability (P=0.026) and increased intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels (P<0.001), and induced apoptosis (P<0.01) in the primary astrocytes relative to the NC group. However, in the parecoxib pretreatment groups, all the above changes reversed significantly (P<0.05) as compared to the H2O2 treatment group, and were nearly unchanged when compared to the NC group. Mechanical investigation showed that dysregulated Bax, Bcl-2, and BDNF could be implicated in these changes.
Conclusions: Our results indicated that parecoxib provided a protective effect from oxidative stress induced by exposure to H2O2.
Keywords: Bax; Bcl-2; Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF); Hydrogen peroxide; Parecoxib; Primary astrocyte.
Conflict of interest statement
Compliance with ethics guidelines: Yun-zhi LING, Xiao-hong LI, Li YU, Ye ZHANG, Qi-sheng LIANG, Xiao-di YANG, and Hong-tao WANG declare that they have no conflict of interest. All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Idebenone prevents human optic nerve head astrocytes from oxidative stress, apoptosis, and senescence by stabilizing BAX/Bcl-2 ratio.J Glaucoma. 2013 Jun-Jul;22(5):404-12. doi: 10.1097/IJG.0b013e31824caf90. J Glaucoma. 2013. PMID: 23661043
-
Insulin on hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress involves ROS/Ca2+ and Akt/Bcl-2 signaling pathways.Free Radic Res. 2014 Mar;48(3):347-56. doi: 10.3109/10715762.2013.869588. Epub 2014 Jan 7. Free Radic Res. 2014. PMID: 24286466
-
Melatonin prevents hydrogen peroxide-induced Bax expression in cultured rat astrocytes.J Pineal Res. 2005 Mar;38(2):84-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2004.00166.x. J Pineal Res. 2005. PMID: 15683462
-
[6]-shogaol attenuates neuronal apoptosis in hydrogen peroxide-treated astrocytes through the up-regulation of neurotrophic factors.Phytother Res. 2013 Dec;27(12):1795-9. doi: 10.1002/ptr.4946. Epub 2013 Feb 11. Phytother Res. 2013. PMID: 23401228
-
[Effect of carboxymethylated chitosan on apoptosis and expression of brain derived neurotrophic factor and glial cell line derived neurotrophic factor in oxidative stress induced Schwann cells in vitro].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014 Dec;28(12):1530-5. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25826901 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Antioxidant Effects of Oleuropein on Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Neuronal Stress- An In Vitro Study.Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2020;19(1):74-84. doi: 10.2174/1871523018666190201145824. Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 30714532 Free PMC article.
-
Parecoxib mitigates lung ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation and up-regulating HO-1 expression.Acta Cir Bras. 2021 Oct 25;36(9):e360901. doi: 10.1590/ACB360901. eCollection 2021. Acta Cir Bras. 2021. PMID: 34705944 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibitors on Kynurenic Acid Production in Rat Brain in Vitro.Neurotox Res. 2019 Jan;35(1):244-254. doi: 10.1007/s12640-018-9952-9. Epub 2018 Sep 3. Neurotox Res. 2019. PMID: 30178287 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of DAAO Overexpression in Delayed Hippocampal Neuronal Death.Cells. 2022 Nov 21;11(22):3689. doi: 10.3390/cells11223689. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36429117 Free PMC article.
References
-
- An LN, Yue Y, Guo WZ, et al. Surgical trauma induces iron accumulation and oxidative stress in a rodent model of postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2013;151(2):277–283. (Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12011-012-9564-9) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arora SS, Gooch JL, Garcia PS. Postoperative cognitive dysfunction, Alzheimer’s disease, and anesthesia. Int J Neurosci. 2014;124(4):236–242. (Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/00207454.2013.833919) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barres BA. The mystery and magic of glia: a perspective on their roles in health and disease. Neuron. 2008;60(3):430–440. - PubMed
-
- Cao Y, Jiang Z, Zeng Z, et al. Bcl-2 silencing attenuates hypoxia-induced apoptosis resistance in pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells. Apoptosis. 2016;21(1):69–84. (Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10495-015-1184-3) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Guan JJ, Zhang XD, Sun W, et al. DRAM1 regulates apoptosis through increasing protein levels and lysosomal localization of BAX. Cell Death Dis. 2015;6:e1624. (Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2014.546) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

