Therapeutic TNF Inhibitors can Differentially Stabilize Trimeric TNF by Inhibiting Monomer Exchange
- PMID: 27605058
- PMCID: PMC5015024
- DOI: 10.1038/srep32747
Therapeutic TNF Inhibitors can Differentially Stabilize Trimeric TNF by Inhibiting Monomer Exchange
Abstract
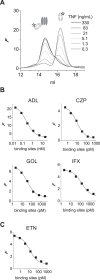
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is a homotrimeric cytokine that is a key mediator of inflammation. It is unstable at physiological concentrations and slowly converts into an inactive form. Here, we investigated the mechanism of this process by using a Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) assay that allowed monitoring of monomeric subunit exchange in time. We observed continuous exchange of monomeric subunits even at concentrations of TNF high enough to maintain its bioactivity. The kinetics of this process closely corresponds with the appearance of monomeric subunits and disappearance of trimeric TNF in time at ng/ml concentrations as monitored by high-performance size-exclusion chromatography (HP-SEC). Furthermore, of the five therapeutic TNF inhibitors that are currently used in the clinic, three (adalimumab, infliximab, etanercept) were found to completely inhibit the monomer exchange reaction and stabilize TNF trimers, whereas golimumab and certolizumab could not prevent monomer exchange, but did slow down the exchange process. These differences were not correlated with the affinities of the TNF inhibitors, measured with both surface plasmon resonance (SPR) and in fluid phase using fluorescence-assisted HP-SEC. The stabilizing effect of these TNF inhibitors might result in prolonged residual TNF bioactivity under conditions of incomplete blocking, as observed in vitro for adalimumab.
Conflict of interest statement
GJW has received a research grant from Pfizer and honoraria for lectures fromAbbvie, Pfizer and UCB. TR has received honoraria for lectures from Pfizer and Abbvie.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The trimer to monomer transition of Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha is a dynamic process that is significantly altered by therapeutic antibodies.Sci Rep. 2020 Jun 9;10(1):9265. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-66123-5. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32518229 Free PMC article.
-
Comparisons of affinities, avidities, and complement activation of adalimumab, infliximab, and etanercept in binding to soluble and membrane tumor necrosis factor.Clin Immunol. 2009 May;131(2):308-16. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2009.01.002. Epub 2009 Feb 1. Clin Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19188093
-
Whole cell-based surface plasmon resonance measurement to assess binding of anti-TNF agents to transmembrane target.Anal Biochem. 2016 Sep 1;508:73-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2016.06.021. Epub 2016 Jun 24. Anal Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27349512
-
[TNF inhibitors].Nihon Rinsho. 2016 Jun;74(6):957-62. Nihon Rinsho. 2016. PMID: 27311185 Review. Japanese.
-
Therapeutic Potential of TNF-α Inhibition for Alzheimer's Disease Prevention.J Alzheimers Dis. 2020;78(2):619-626. doi: 10.3233/JAD-200711. J Alzheimers Dis. 2020. PMID: 33016914 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An Anti-hTNF-α Variable New Antigen Receptor Format Demonstrates Superior in vivo Preclinical Efficacy to Humira® in a Transgenic Mouse Autoimmune Polyarthritis Disease Model.Front Immunol. 2019 Mar 22;10:526. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00526. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30967865 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Basis for How Biologic Medicines Bind their Targets in Psoriasis Therapy.Yale J Biol Med. 2020 Mar 27;93(1):19-27. eCollection 2020 Mar. Yale J Biol Med. 2020. PMID: 32226331 Free PMC article.
-
Serum TNFα levels at 24 h after certolizumab pegol predict effectiveness at week 12 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis from TSUBAME study.Arthritis Res Ther. 2021 Jun 1;23(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s13075-021-02547-2. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34074349 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Tumor Necrosis Factor α Blockade: An Opportunity to Tackle Breast Cancer.Front Oncol. 2020 Apr 22;10:584. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00584. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32391269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PET/CT Imaging of Human TNFα Using [89Zr]Certolizumab Pegol in a Transgenic Preclinical Model of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Mol Imaging Biol. 2020 Feb;22(1):105-114. doi: 10.1007/s11307-019-01363-0. Mol Imaging Biol. 2020. PMID: 31065895
References
-
- Eck M. J. & Sprang S. R. The structure of tumor necrosis factor-alpha at 2.6 A resolution. Implications for receptor binding. J. Biol. Chem. 264, 17595–17605 (1989). - PubMed
-
- Pennica D. et al. Biochemical characterization of the extracellular domain of the 75-kilodalton tumor necrosis factor receptor. Biochemistry 32, 3131–3138 (1993). - PubMed
-
- Loetscher H., Gentz R., Zulauf M., Lustig A., Tabuchi H. et al. Recombinant 55-kDa tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor. Stoichiometry of binding to TNF alpha and TNF beta and inhibition of TNF activity. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 18324–18329 (1991). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

