A Non-catalytic Deep Desulphurization Process using Hydrodynamic Cavitation
- PMID: 27605492
- PMCID: PMC5015108
- DOI: 10.1038/srep33021
A Non-catalytic Deep Desulphurization Process using Hydrodynamic Cavitation
Abstract
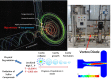
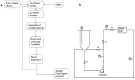
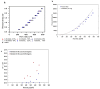
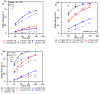
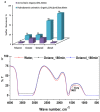
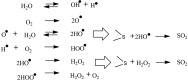
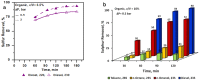
A novel approach is developed for desulphurization of fuels or organics without use of catalyst. In this process, organic and aqueous phases are mixed in a predefined manner under ambient conditions and passed through a cavitating device. Vapor cavities formed in the cavitating device are then collapsed which generate (in-situ) oxidizing species which react with the sulphur moiety resulting in the removal of sulphur from the organic phase. In this work, vortex diode was used as a cavitating device. Three organic solvents (n-octane, toluene and n-octanol) containing known amount of a model sulphur compound (thiophene) up to initial concentrations of 500 ppm were used to verify the proposed method. A very high removal of sulphur content to the extent of 100% was demonstrated. The nature of organic phase and the ratio of aqueous to organic phase were found to be the most important process parameters. The results were also verified and substantiated using commercial diesel as a solvent. The developed process has great potential for deep of various organics, in general, and for transportation fuels, in particular.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare competing financial interests. Intellectual property pertaining to the materials presented in this Report is protected by two patents (WO 2013054362 A2 20130418; 2015-INV-0092: 0230NF2015).
Figures
References
-
- Bhandari V. M. et al.. Desulphurization of diesel using ion-exchanged zeolites. Chemical Engineering Science 61, 2599–2608 (2006).
-
- Song C. An overview of new approaches to deep desulphurization for ultra-clean gasoline, diesel fuel and jet fuel. Catalysis Today 86, 211–263 (2003).
-
- Yang R. T., Hernández-Maldonado A. J. & Yang F. H. Desulphurization of transportation fuels with zeolites under ambient conditions. Science (New York, NY) 301, 79–81 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Song C. & Ma X. New design approaches to ultra-clean diesel fuels by deep desulphurization and deep dearomatization. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental 41, 207–238 (2003).
-
- Chandra Srivastava V. An evaluation of desulphurization technologies for sulphur removal from liquid fuels. RSC Adv. 2, 759–783 (2012).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

