Auditory Cortex Characteristics in Schizophrenia: Associations With Auditory Hallucinations
- PMID: 27605526
- PMCID: PMC5216858
- DOI: 10.1093/schbul/sbw130
Auditory Cortex Characteristics in Schizophrenia: Associations With Auditory Hallucinations
Abstract
Background: Neuroimaging studies have demonstrated associations between smaller auditory cortex volume and auditory hallucinations (AH) in schizophrenia. Reduced cortical volume can result from a reduction of either cortical thickness or cortical surface area, which may reflect different neuropathology. We investigate for the first time how thickness and surface area of the auditory cortex relate to AH in a large sample of schizophrenia spectrum patients.
Methods: Schizophrenia spectrum (n = 194) patients underwent magnetic resonance imaging. Mean cortical thickness and surface area in auditory cortex regions (Heschl's gyrus [HG], planum temporale [PT], and superior temporal gyrus [STG]) were compared between patients with (AH+, n = 145) and without (AH-, n = 49) a lifetime history of AH and 279 healthy controls.
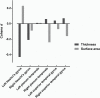
Results: AH+ patients showed significantly thinner cortex in the left HG compared to AH- patients (d = 0.43, P = .0096). There were no significant differences between AH+ and AH- patients in cortical thickness in the PT or STG, or in auditory cortex surface area in any of the regions investigated. Group differences in cortical thickness in the left HG was not affected by duration of illness or current antipsychotic medication.
Conclusions: AH in schizophrenia patients were related to thinner cortex, but not smaller surface area of the left HG, a region which includes the primary auditory cortex. The results support that structural abnormalities of the auditory cortex underlie AH in schizophrenia.
Keywords: Heschl’s gyrus; cortical surface area; cortical thickness; magnetic resonance imaging; neuroimaging; psychosis.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Maryland Psychiatric Research Center. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional connectivity of left Heschl's gyrus in vulnerability to auditory hallucinations in schizophrenia.Schizophr Res. 2013 Feb;143(2-3):260-8. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2012.11.037. Epub 2012 Dec 31. Schizophr Res. 2013. PMID: 23287311 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical thickness abnormalities in bipolar disorder patients with a lifetime history of auditory hallucinations.Bipolar Disord. 2018 Nov;20(7):647-657. doi: 10.1111/bdi.12627. Epub 2018 Feb 13. Bipolar Disord. 2018. PMID: 29441665
-
Abnormal dynamic functional connectivity between speech and auditory areas in schizophrenia patients with auditory hallucinations.Neuroimage Clin. 2018 Jun 18;19:918-924. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2018.06.018. eCollection 2018. Neuroimage Clin. 2018. PMID: 30003029 Free PMC article.
-
Auditory cortex asymmetry, altered minicolumn spacing and absence of ageing effects in schizophrenia.Brain. 2008 Dec;131(Pt 12):3178-92. doi: 10.1093/brain/awn211. Epub 2008 Sep 26. Brain. 2008. PMID: 18819990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Associations between cortical thickness and auditory verbal hallucinations in patients with schizophrenia: A systematic review.Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging. 2018 Dec 30;282:31-39. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2018.10.005. Epub 2018 Oct 22. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging. 2018. PMID: 30384148
Cited by
-
Functional Connectivity of the Auditory Cortex in Women With Trauma-Related Disorders Who Hear Voices.Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2024 Oct;9(10):1066-1074. doi: 10.1016/j.bpsc.2024.06.009. Epub 2024 Jun 27. Biol Psychiatry Cogn Neurosci Neuroimaging. 2024. PMID: 38944384
-
Neural Correlates of Positive and Negative Formal Thought Disorder in Individuals with Schizophrenia: An ENIGMA Schizophrenia Working Group Study.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Sep 28:rs.3.rs-3179362. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3179362/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Mol Psychiatry. 2024 Oct;29(10):3086-3096. doi: 10.1038/s41380-024-02563-z. PMID: 37841855 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Auditory Cortex Thickness Is Associated With N100 Amplitude in Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorders.Schizophr Bull Open. 2023 Jun 9;4(1):sgad015. doi: 10.1093/schizbullopen/sgad015. eCollection 2023 Jan 1. Schizophr Bull Open. 2023. PMID: 38812720 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying Schizophrenia Using Structural MRI With a Deep Learning Algorithm.Front Psychiatry. 2020 Feb 3;11:16. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00016. eCollection 2020. Front Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32116837 Free PMC article.
-
Shared atypical spontaneous brain activity pattern in early onset schizophrenia and autism spectrum disorders: evidence from cortical surface-based analysis.Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2024 Jul;33(7):2387-2396. doi: 10.1007/s00787-023-02333-2. Epub 2023 Dec 26. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38147111 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lim A, Hoek HW, Deen ML, Blom JD, Investigators G. Prevalence and classification of hallucinations in multiple sensory modalities in schizophrenia spectrum disorders [published online ahead of print June 24, 2016]. Schizophr Res. 2016. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2016.06.010. - PubMed
-
- Goghari VM, Harrow M, Grossman LS, Rosen C. A 20-year multi-follow-up of hallucinations in schizophrenia, other psychotic, and mood disorders. Psychol Med. 2013;43:1151–1160. - PubMed
-
- Goghari VM, Harrow M. Twenty year multi-follow-up of different types of hallucinations in schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder, bipolar disorder, and depression [published online ahead of print June 24, 2016]. Schizophr Res. 2016. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2016.06.027. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases