Heat shock protein-based therapy as a potential candidate for treating the sphingolipidoses
- PMID: 27605553
- PMCID: PMC6821533
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aad9823
Heat shock protein-based therapy as a potential candidate for treating the sphingolipidoses
Abstract
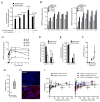
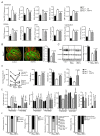
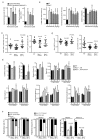
Lysosomal storage diseases (LSDs) often manifest with severe systemic and central nervous system (CNS) symptoms. The existing treatment options are limited and have no or only modest efficacy against neurological manifestations of disease. We demonstrate that recombinant human heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) improves the binding of several sphingolipid-degrading enzymes to their essential cofactor bis(monoacyl)glycerophosphate in vitro. HSP70 treatment reversed lysosomal pathology in primary fibroblasts from 14 patients with eight different LSDs. HSP70 penetrated effectively into murine tissues including the CNS and inhibited glycosphingolipid accumulation in murine models of Fabry disease (Gla(-/-)), Sandhoff disease (Hexb(-/-)), and Niemann-Pick disease type C (Npc1(-/-)) and attenuated a wide spectrum of disease-associated neurological symptoms in Hexb(-/-) and Npc1(-/-) mice. Oral administration of arimoclomol, a small-molecule coinducer of HSPs that is currently in clinical trials for Niemann-Pick disease type C (NPC), recapitulated the effects of recombinant human HSP70, suggesting that heat shock protein-based therapies merit clinical evaluation for treating LSDs.
Copyright © 2016, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Comment in
-
Lysosomal storage diseases: HSP70 reverses lysosomal pathology.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016 Nov 3;15(11):750. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2016.220. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016. PMID: 27807363 No abstract available.
References
-
- Parenti G, Andria G, Ballabio A. Lysosomal Storage Diseases: From Pathophysiology to Therapy. Annu Rev Med. 2015;66:471–486. - PubMed
-
- Muchowski PJ, Wacker JL. Modulation of neurodegeneration by molecular chaperones. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005;6:11–22. - PubMed
-
- Kieran D, Kalmar B, Dick JRT, Riddoch-Contreras J, Burnstock G, Greensmith L. Treatment with arimoclomol, a coinducer of heat shock proteins, delays disease progression in ALS mice. Nat Med. 2004;10:402–405. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

