Reactivation of Rate Remapping in CA3
- PMID: 27605610
- PMCID: PMC6601871
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1678-15.2016
Reactivation of Rate Remapping in CA3
Abstract
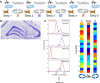
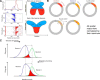
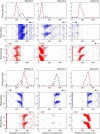
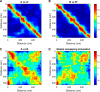
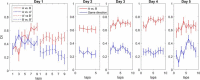
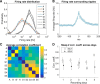
The hippocampus is thought to contribute to episodic memory by creating, storing, and reactivating patterns that are unique to each experience, including different experiences that happen at the same location. Hippocampus can combine spatial and contextual/episodic information using a dual coding scheme known as "global" and "rate" remapping. Global remapping selects which set of neurons can activate at a given location. Rate remapping readjusts the firing rates of this set depending on current experience, thus expressing experience-unique patterns at each location. But can the experience-unique component be retrieved spontaneously? Whereas reactivation of recent, spatially selective patterns in hippocampus is well established, it is never perfect, raising the issue of whether the experiential component might be absent. This question is key to the hypothesis that hippocampus can assist memory consolidation by reactivating and broadcasting experience-specific "index codes" to neocortex. In CA3, global remapping exhibits attractor-like dynamics, whereas rate remapping apparently does not, leading to the hypothesis that only the former can be retrieved associatively and casting doubt on the general consolidation hypothesis. Therefore, we studied whether the rate component is reactivated spontaneously during sleep. We conducted neural ensemble recordings from CA3 while rats ran on a circular track in different directions (in different sessions) and while they slept. It was shown previously that the two directions of running result in strong rate remapping. During sleep, the most recent rate distribution was reactivated preferentially. Therefore, CA3 can retrieve patterns spontaneously that are unique to both the location and the content of recent experience.
Significance statement: The hippocampus is required for memory of events and their spatial contexts. The primary correlate of hippocampal activity is location in space, but multiple memories can occur in the same location. To be useful for distinguishing these memories, the hippocampus must be able, not only to express, but also to retrieve both spatial and nonspatial information about events. Whether it can retrieve nonspatial information has been challenged recently. We exposed rats to two different experiences (running in different directions) in the same locations and showed that even the nonspatial components of hippocampal cell firing are reactivated spontaneously during sleep, supporting the conclusion that both types of information about a recent experience can be retrieved.
Keywords: CA3; episodic memory; hippocampus; memory reactivation; rate remapping.
Copyright © 2016 the authors 0270-6474/16/369342-09$15.00/0.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fast rate coding in hippocampal CA3 cell ensembles.Hippocampus. 2006;16(9):765-74. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20201. Hippocampus. 2006. PMID: 16888744
-
Time Cells in Hippocampal Area CA3.J Neurosci. 2016 Jul 13;36(28):7476-84. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0087-16.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27413157 Free PMC article.
-
Place cell rate remapping by CA3 recurrent collaterals.PLoS Comput Biol. 2014 Jun 5;10(6):e1003648. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003648. eCollection 2014 Jun. PLoS Comput Biol. 2014. PMID: 24902003 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal place cells, context, and episodic memory.Hippocampus. 2006;16(9):716-29. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20208. Hippocampus. 2006. PMID: 16897724 Review.
-
Hippocampal place cells: parallel input streams, subregional processing, and implications for episodic memory.Hippocampus. 2006;16(9):755-64. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20203. Hippocampus. 2006. PMID: 16883558 Review.
Cited by
-
Distinct neural mechanisms for heading retrieval and context recognition in the hippocampus during spatial reorientation.Nat Commun. 2024 Jul 16;15(1):5968. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-50112-7. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39013846 Free PMC article.
-
Transformation of spatial representations along hippocampal circuits.iScience. 2024 Jun 24;27(7):110361. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110361. eCollection 2024 Jul 19. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39071886 Free PMC article.
-
Replay, the default mode network and the cascaded memory systems model.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2022 Oct;23(10):628-640. doi: 10.1038/s41583-022-00620-6. Epub 2022 Aug 15. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35970912 Review.
-
Experience-driven rate modulation is reinstated during hippocampal replay.Elife. 2022 Aug 22;11:e79031. doi: 10.7554/eLife.79031. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35993533 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal neurons construct a map of an abstract value space.Cell. 2021 Sep 2;184(18):4640-4650.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.07.010. Epub 2021 Aug 3. Cell. 2021. PMID: 34348112 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
