Maternal Rest/Nrsf Regulates Zebrafish Behavior through snap25a/b
- PMID: 27605615
- PMCID: PMC5013188
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1246-16.2016
Maternal Rest/Nrsf Regulates Zebrafish Behavior through snap25a/b
Abstract
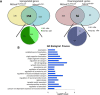
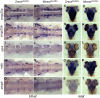
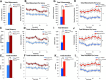
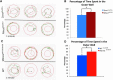
During embryonic development, regulation of gene expression is key to creating the many subtypes of cells that an organism needs throughout its lifetime. Recent work has shown that maternal genetics and environmental factors have lifelong consequences on diverse processes ranging from immune function to stress responses. The RE1-silencing transcription factor (Rest) is a transcriptional repressor that interacts with chromatin-modifying complexes to repress transcription of neural-specific genes during early development. Here we show that in zebrafish, maternally supplied rest regulates expression of target genes during larval development and has lifelong impacts on behavior. Larvae deprived of maternal rest are hyperactive and show atypical spatial preferences. Adult male fish deprived of maternal rest present with atypical spatial preferences in a novel environment assay. Transcriptome sequencing revealed 158 genes that are repressed by maternal rest in blastula stage embryos. Furthermore, we found that maternal rest is required for target gene repression until at least 6 dpf. Importantly, disruption of the RE1 sites in either snap25a or snap25b resulted in behaviors that recapitulate the hyperactivity phenotype caused by absence of maternal rest Both maternal rest mutants and snap25a RE1 site mutants have altered primary motor neuron architecture that may account for the enhanced locomotor activity. These results demonstrate that maternal rest represses snap25a/b to modulate larval behavior and that early Rest activity has lifelong behavioral impacts.
Significance statement: Maternal factors deposited in the oocyte have well-established roles during embryonic development. We show that, in zebrafish, maternal rest (RE1-silencing transcription factor) regulates expression of target genes during larval development and has lifelong impacts on behavior. The Rest transcriptional repressor interacts with chromatin-modifying complexes to limit transcription of neural genes. We identify several synaptic genes that are repressed by maternal Rest and demonstrate that snap25a/b are key targets of maternal rest that modulate larval locomotor activity. These results reveal that zygotic rest is unable to compensate for deficits in maternally supplied rest and uncovers novel temporal requirements for Rest activity, which has implications for the broad roles of Rest-mediated repression during neural development and in disease states.
Keywords: Rest/Nrsf; locomotor behavior; maternal effect; snap25; zebrafish.
Copyright © 2016 the authors 0270-6474/16/369407-13$15.00/0.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Rest mutant zebrafish swim erratically and display atypical spatial preferences.Behav Brain Res. 2015 May 1;284:238-48. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2015.02.026. Epub 2015 Feb 21. Behav Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25712696 Free PMC article.
-
Rest represses maturation within migrating facial branchiomotor neurons.Dev Biol. 2015 May 15;401(2):220-35. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2015.02.021. Epub 2015 Mar 11. Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 25769695 Free PMC article.
-
Zebrafish rest regulates developmental gene expression but not neurogenesis.Development. 2012 Oct;139(20):3838-48. doi: 10.1242/dev.080994. Epub 2012 Sep 5. Development. 2012. PMID: 22951640 Free PMC article.
-
Knockout of REST/NRSF shows that the protein is a potent repressor of neuronally expressed genes in non-neural tissues.Bioessays. 1999 May;21(5):372-6. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-1878(199905)21:5<372::AID-BIES3>3.0.CO;2-3. Bioessays. 1999. PMID: 10376008 Review.
-
REST Is Not Resting: REST/NRSF in Health and Disease.Biomolecules. 2023 Oct 2;13(10):1477. doi: 10.3390/biom13101477. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37892159 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Parentally inherited long non-coding RNA Cyrano is involved in zebrafish neurodevelopment.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Oct 12;46(18):9726-9735. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky628. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 30011017 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-210-5p Contributes to Cognitive Impairment in Early Vascular Dementia Rat Model Through Targeting Snap25.Front Mol Neurosci. 2018 Nov 13;11:388. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00388. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30483048 Free PMC article.
-
mGluR5 regulates REST/NRSF signaling through N-cadherin/β-catenin complex in Huntington's disease.Mol Brain. 2020 Aug 28;13(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s13041-020-00657-7. Mol Brain. 2020. PMID: 32859226 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and distribution of synaptotagmin family members in the zebrafish retina.J Comp Neurol. 2022 Mar;530(4):705-728. doi: 10.1002/cne.25238. Epub 2021 Sep 24. J Comp Neurol. 2022. PMID: 34468021 Free PMC article.
-
Zebrafish sin3b mutants are viable but have size, skeletal, and locomotor defects.Dev Dyn. 2017 Nov;246(11):946-955. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.24581. Epub 2017 Sep 25. Dev Dyn. 2017. PMID: 28850761 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ballas N, Battaglioli E, Atouf F, Andres ME, Chenoweth J, Anderson ME, Burger C, Moniwa M, Davie JR, Bowers WJ, Federoff HJ, Rose DW, Rosenfeld MG, Brehm P, Mandel G. Regulation of neuronal traits by a novel transcriptional complex. Neuron. 2001;31:353–365. doi: 10.1016/S0896-6273(01)00371-3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bruce AW, Donaldson IJ, Wood IC, Yerbury SA, Sadowski MI, Chapman M, Göttgens B, Buckley NJ. Genome-wide analysis of repressor element 1 silencing transcription factor/neuron-restrictive silencing factor (REST/NRSF) target genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:10458–10463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0401827101. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
