Cross-regulation of Phosphodiesterase 1 and Phosphodiesterase 2 Activities Controls Dopamine-mediated Striatal α-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic Acid (AMPA) Receptor Trafficking
- PMID: 27605670
- PMCID: PMC5087742
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.749747
Cross-regulation of Phosphodiesterase 1 and Phosphodiesterase 2 Activities Controls Dopamine-mediated Striatal α-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic Acid (AMPA) Receptor Trafficking
Abstract
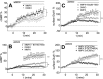
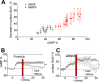
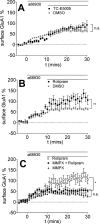
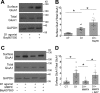
Dopamine, a key striatal neuromodulator, increases synaptic strength by promoting surface insertion and/or retention of AMPA receptors (AMPARs). This process is mediated by the phosphorylation of the GluA1 subunit of AMPAR by cyclic nucleotide-dependent kinases, making cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases (PDEs) potential regulators of synaptic strength. In this study, we examined the role of phosphodiesterase 2 (PDE2), a medium spiny neuron-enriched and cGMP-activated PDE, in AMPAR trafficking. We found that inhibiting PDE2 resulted in enhancement of dopamine-induced surface GluA1 expression in dopamine receptor 1-expressing medium spiny neurons. Using pharmacological and genetic approaches, we found that inhibition of PDE1 resulted in a decrease in surface AMPAR levels because of the allosteric activation of PDE2. The cross-regulation of PDE1 and PDE2 activities results in counterintuitive control of surface AMPAR expression, making it possible to regulate the directionality and magnitude of AMPAR trafficking.
Keywords: AMPA receptor (AMPAR); GluA1; PDE1; PDE2; cAMP; cGMP; dopamine; phosphodiesterases; trafficking.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Graybiel A. M. (2005) The basal ganglia: learning new tricks and loving it. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 15, 638–644 - PubMed
-
- Surmeier D. J., Ding J., Day M., Wang Z., and Shen W. (2007) D1 and D2 dopamine-receptor modulation of striatal glutamatergic signaling in striatal medium spiny neurons. Trends Neurosci. 30, 228–235 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

