Pathophysiological role of guanylate-binding proteins in gastrointestinal diseases
- PMID: 27605879
- PMCID: PMC4968125
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i28.6434
Pathophysiological role of guanylate-binding proteins in gastrointestinal diseases
Abstract
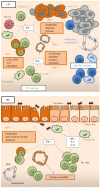
Guanylate-binding proteins (GBPs) are interferon-stimulated factors involved in the defense against cellular pathogens and inflammation. These proteins, particularly GBP-1, the most prominent member of the family, have been established as reliable markers of interferon-γ-activated cells in various diseases, including colorectal carcinoma (CRC) and inflammatory bowel diseases (IBDs). In CRC, GBP-1 expression is associated with a Th1-dominated angiostatic micromilieu and is correlated with a better outcome. Inhibition of tumor growth by GBP-1 is the result of its strong anti-angiogenic activity as well as its direct anti-tumorigenic effect on tumor cells. In IBD, GBP-1 mediates the anti-proliferative effects of interferon-γ on intestinal epithelial cells. In addition, it plays a protective role on the mucosa by preventing cell apoptosis, by inhibiting angiogenesis and by regulating the T-cell receptor signaling. These functions rely to a large extent on the ability of GBP-1 to interact with and remodel the actin cytoskeleton.
Keywords: Colorectal carcinoma; Guanylate-binding proteins; Inflammatory bowel diseases; Interferon.
Figures

References
-
- Ghosh A, Praefcke GJ, Renault L, Wittinghofer A, Herrmann C. How guanylate-binding proteins achieve assembly-stimulated processive cleavage of GTP to GMP. Nature. 2006;440:101–104. - PubMed
-
- Vöpel T, Syguda A, Britzen-Laurent N, Kunzelmann S, Lüdemann MB, Dovengerds C, Stürzl M, Herrmann C. Mechanism of GTPase-activity-induced self-assembly of human guanylate binding protein 1. J Mol Biol. 2010;400:63–70. - PubMed
-
- Wehner M, Kunzelmann S, Herrmann C. The guanine cap of human guanylate-binding protein 1 is responsible for dimerization and self-activation of GTP hydrolysis. FEBS J. 2012;279:203–210. - PubMed
-
- Cheng YS, Colonno RJ, Yin FH. Interferon induction of fibroblast proteins with guanylate binding activity. J Biol Chem. 1983;258:7746–7750. - PubMed
-
- Lubeseder-Martellato C, Guenzi E, Jörg A, Töpolt K, Naschberger E, Kremmer E, Zietz C, Tschachler E, Hutzler P, Schwemmle M, et al. Guanylate-binding protein-1 expression is selectively induced by inflammatory cytokines and is an activation marker of endothelial cells during inflammatory diseases. Am J Pathol. 2002;161:1749–1759. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

