Specific immunotherapy with mugwort pollen allergoid reduce bradykinin release into the nasal fluid
- PMID: 27605897
- PMCID: PMC5004215
- DOI: 10.5114/ada.2016.61602
Specific immunotherapy with mugwort pollen allergoid reduce bradykinin release into the nasal fluid
Abstract
Introduction: A pathomechanism of allergic rhinitis is complex. A neurogenic mechanism seems to play a significant role in this phenomenon.
Aim: The evaluation of influence of specific immunotherapy of mugwort pollen allergic patients on the bradykinin concentration in the nasal lavage fluid.
Material and methods: The study included 22 seasonal allergic rhinitis patients. Thirty persons with monovalent allergy to mugwort pollen, confirmed with skin prick tests and allergen-specific immunoglobulin E, underwent a 3-year-long allergen immunotherapy with the mugwort extract (Allergovit, Allergopharma, Germany). The control group was composed of 9 persons with polyvalent sensitivity to pollen, who were treated with pharmacotherapy. Before the allergen-specific immunotherapy (AIT) and in subsequent years before the pollen seasons, a provocation allergen test with the mugwort extract was performed, together with collection of nasal fluids, where bradykinin concentration was determined according to Proud method.
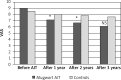
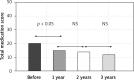
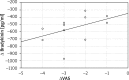
Results: There were similar levels of bradykinin in both groups at baseline prior to therapy (AIT group: 584.0 ±87.2 vs. controls 606.3 ±106.5 pg/ml) and changes after allergen challenge 1112.4 ±334.8 vs. 1013.3 ±305.9 pg/ml as well. The bradykinin concentration in nasal lavage fluid after mugwort challenge in 1 year was lower in the AIT group (824.1 ±184.2 pg/ml vs. 1000.4 ±411.5 pg/l; p < 005) with a further significant decrease after the 2(nd) and 3(rd) year of specific immunotherapy. Significant reduction of symptoms and medications use was observed in hyposensitized patients.
Conclusions: A decreased level of bradykinin as a result of AIT suggests that some of the symptomatic benefits of AIT may be related to the reduced release of bradykinin into nasal secretions. These values correlate with clinical improvement within the course of treatment.
Keywords: allergen immunotherapy; bradykinin; mugwort; nasal lavage; seasonal allergic rhinitis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Endothelin-1 and bradykinin in nasal lavage fluid of patients allergic to tree pollen].Otolaryngol Pol. 2002;56(1):11-7. Otolaryngol Pol. 2002. PMID: 12053657 Clinical Trial. Polish.
-
The effects of grass pollen allergoid immunotherapy on clinical and immunological parameters in children with allergic rhinitis.Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2006 Sep;17(6):396-407. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3038.2006.00442.x. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16925684 Clinical Trial.
-
Immunologic effects and tolerability profile of in-season initiation of a standardized-quality grass allergy immunotherapy tablet: a phase III, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in adults with grass pollen-induced rhinoconjunctivitis.Clin Ther. 2011 Jul;33(7):828-40. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2011.06.006. Epub 2011 Jul 7. Clin Ther. 2011. PMID: 21741092 Clinical Trial.
-
[Rhinitis in adults].Acta Med Croatica. 2011;65(2):181-7. Acta Med Croatica. 2011. PMID: 22359885 Review. Croatian.
-
Allergen immunotherapy phase II trials: Challenges in dose finding.Allergol Select. 2019 Dec 30;3(1):1-8. doi: 10.5414/ALX02033E. eCollection 2019. Allergol Select. 2019. PMID: 32176223 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of substance P and bradykinin levels in nasal secretions of patients with nasal polyposis with and without sensitivity to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2022 Jun 29;7(4):928-934. doi: 10.1002/lio2.851. eCollection 2022 Aug. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2022. PMID: 36000030 Free PMC article.
-
[Allergen immunotherapy for rare allergens].HNO. 2024 Sep;72(9):626-632. doi: 10.1007/s00106-024-01469-0. Epub 2024 Apr 19. HNO. 2024. PMID: 38639764 Review. German.
References
-
- Akdis M, Akdis CA. Mechanisms of allergen-specific immunotherapy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007;119:780–91. - PubMed
-
- Mailing HJ, Bousquet J. Subcutaneous immunotherapy for allergic rhinoconjunctivitis, allergic asthma, and prevention of allergic diseases. Clin Allergy Immunol. 2008;21:343–5. - PubMed
-
- Zuberbier T, Bachert C, Bousquet PJ, et al. GA(2)LEN/EAACI pocket guide for allergen-specific immunotherapy for allergic rhinitis and asthma. Allergy. 2010;65:1525–30. - PubMed
-
- Gawlik R. The role of neuropeptides in pathophysiology of rhinitis. Postep Dermatol Alergol. 2010;27:162–5.
-
- Mossiman BL, White M, Hohman R, et al. Substance P, CGRP, and vasoactive intestinal peptide increase in nasal secretions after allergen challenge in atopic patients. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1993;92:95–104. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
