A 3 Year-Old Male Child Ingested Approximately 750 Grams of Elemental Mercury
- PMID: 27606146
- PMCID: PMC5001828
- DOI: 10.5152/balkanmedj.2016.15197
A 3 Year-Old Male Child Ingested Approximately 750 Grams of Elemental Mercury
Abstract
Background: The oral ingestion of elemental mercury is unlikely to cause systemic toxicity, as it is poorly absorbed through the gastrointestinal system. However, abnormal gastrointestinal function or anatomy may allow elemental mercury into the bloodstream and the peritoneal space. Systemic effects of massive oral intake of mercury have rarely been reported.
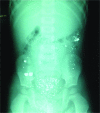
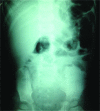
Case report: In this paper, we are presenting the highest single oral intake of elemental mercury by a child aged 3 years. A Libyan boy aged 3 years ingested approximately 750 grams of elemental mercury and was still asymptomatic.
Conclusion: The patient had no existing disease or abnormal gastrointestinal function or anatomy. The physical examination was normal. His serum mercury level was 91 µg/L (normal: <5 µg/L), and he showed no clinical manifestations. Exposure to mercury in children through different circumstances remains a likely occurrence.
Keywords: Intoxication; mercury; supportive therapy.
Figures
References
-
- Boyd AS, Seger D, Vannucci S, Langley M, Abraham JL, King LE., Jr Mercury exposure and cutaneous disease. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;43:81–90. http://dx.doi.org/10.1067/mjd.2000.106360. - DOI - PubMed
-
- McKay CA, Perez A, Goldstein R. Mercury. In: Erickson TB, Baum CR, Ling LJ, editors. Pediatric Toxicology: Diagnosis and Management of the Poisoned Child. NewYork, PA: The McGraw-Hill Companies; 2005. pp. 468–75.
-
- Kolkhorst KS, Kulkarni PM. Accidental metallic mercury ingestion. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2012;112:381. - PubMed
-
- Mahajan PV. Heavy Metal Intoxication Mercury. In: Kliegman RM, Geme JW, Schor NF, Behrman RE, editors. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 19th ed. Philadelphia PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2011. p. 2448. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/B978-1-4377-0755-7.00701-6. - DOI
-
- Carman KB, Tutkun E, Yilmaz H, Dilber C, Dalkiran T, Cakir B, et al. Acute mercury poisoning among children in two provinces of Turkey. Eur J Pediatr. 2013;172:821–7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00431-013-1970-2. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources