Botulinum Toxin A Injection into the Subscapularis Muscle to Treat Intractable Hemiplegic Shoulder Pain
- PMID: 27606265
- PMCID: PMC5012970
- DOI: 10.5535/arm.2016.40.4.592
Botulinum Toxin A Injection into the Subscapularis Muscle to Treat Intractable Hemiplegic Shoulder Pain
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the beneficial effect of botulinum toxin A (Botox) injection into the subscapularis muscle on intractable hemiplegic shoulder pain.
Methods: Six stroke patients with intractable hemiplegic shoulder pain were included. Botulinum toxin A was injected into the subscapularis muscle. Intractable hemiplegic shoulder pain was evaluated using an 11-point numerical rating scale. Pain-free range of motion was assessed for shoulder abduction and external rotation. The spasticity of the shoulder internal rotator was measured using the modified Ashworth scale. Assessments were carried out at baseline and at 1, 2, 4, and, if possible, 8 weeks.
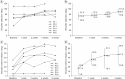
Results: Intractable hemiplegic shoulder pain was improved (p=0.004) after botulinum toxin injection into the subscapularis muscle. Restricted shoulder abduction (p=0.003), external rotation (p=0.005), and spasticity of the shoulder internal rotator (p=0.005) were also improved. Improved hemiplegic shoulder pain was correlated with improved shoulder abduction (r=-1.0, p<0.001), external rotation (r=-1.0, p<0.001), and spasticity of the internal rotator (r=1.0, p<0.001).
Conclusion: Botulinum toxin A injection into the subscapularis muscle appears to be valuable in the management of intractable hemiplegic shoulder pain.
Keywords: Hemiplegia; Intractable pain; Intramuscular injections; Shoulder pain; Type A botulinum toxins.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
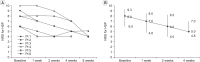

Similar articles
-
Ultrasound-Guided BoNT-A (Botulinum Toxin A) Injection Into the Subscapularis for Hemiplegic Shoulder Pain: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial.Stroke. 2021 Dec;52(12):3759-3767. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.121.034049. Epub 2021 Sep 2. Stroke. 2021. PMID: 34470492 Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment of shoulder pain in spastic hemiplegia by reducing spasticity of the subscapular muscle: a randomised, double blind, placebo controlled study of botulinum toxin A.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2007 Aug;78(8):845-8. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.2006.103341. Epub 2006 Nov 6. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2007. PMID: 17088333 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment of pain and limited movement of the shoulder in hemiplegic patients with botulinum toxin a in the subscapular muscle.Eur Neurol. 2003;50(2):91-3. doi: 10.1159/000072505. Eur Neurol. 2003. PMID: 12944713
-
Effectiveness of Botulinum Toxin A in Treatment of Hemiplegic Shoulder Pain: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2021 Sep;102(9):1775-1787. doi: 10.1016/j.apmr.2020.12.010. Epub 2021 Jan 14. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2021. PMID: 33454279
-
[Painful hemiplegic shoulder in stroke patients: causes and management].Neurologia. 2012 May;27(4):234-44. doi: 10.1016/j.nrl.2011.02.010. Epub 2011 Apr 22. Neurologia. 2012. PMID: 21514698 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Trans-axillary sonography in the ABER (ABduction and External Rotation) position: a window to the subscapularis, teres major and latissimus dorsi.J Ultrasound. 2024 Dec;27(4):963-968. doi: 10.1007/s40477-024-00924-6. Epub 2024 Aug 10. J Ultrasound. 2024. PMID: 39126613
-
Intra-articular injection of botulinum toxin type A for shoulder pain in glenohumeral osteoarthritis: a case series summary and review of the literature.J Pain Res. 2018 Jun 25;11:1239-1245. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S159700. eCollection 2018. J Pain Res. 2018. PMID: 29983587 Free PMC article.
-
The Place of Botulinum Toxin in Spastic Hemiplegic Shoulder Pain after Stroke: A Scoping Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Feb 4;20(4):2797. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20042797. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36833493 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of ultrasound-guided injection of botulinum toxin type A into shoulder joint cavity on shoulder pain in poststroke patients: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2024 Jun 27;25(1):418. doi: 10.1186/s13063-024-08258-8. Trials. 2024. PMID: 38937804 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative study of ultrasonic-guided betamethasone local injection and extracorporeal shock wave therapy in post-stroke hemiplegic shoulder pain: a randomized clinical trial.Front Neurol. 2023 Jul 19;14:1158500. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1158500. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37538259 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adey-Wakeling Z, Arima H, Crotty M, Leyden J, Kleinig T, Anderson CS, et al. Incidence and associations of hemiplegic shoulder pain poststroke: prospective population-based study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2015;96:241–247. - PubMed
-
- Aras MD, Gokkaya NK, Comert D, Kaya A, Cakci A. Shoulder pain in hemiplegia: results from a national rehabilitation hospital in Turkey. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2004;83:713–719. - PubMed
-
- Lo SF, Chen SY, Lin HC, Jim YF, Meng NH, Kao MJ. Arthrographic and clinical findings in patients with hemiplegic shoulder pain. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2003;84:1786–1791. - PubMed
-
- Tavora DG, Gama RL, Bomfim RC, Nakayama M, Silva CE. MRI findings in the painful hemiplegic shoulder. Clin Radiol. 2010;65:789–794. - PubMed
-
- Murie-Fernandez M, Carmona Iragui M, Gnanakumar V, Meyer M, Foley N, Teasell R. Painful hemiplegic shoulder in stroke patients: causes and management. Neurologia. 2012;27:234–244. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

