The Active Metabolite of Warfarin (3'-Hydroxywarfarin) and Correlation with INR, Warfarin and Drug Weekly Dosage in Patients under Oral Anticoagulant Therapy: A Pharmacogenetics Study
- PMID: 27606428
- PMCID: PMC5015920
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162084
The Active Metabolite of Warfarin (3'-Hydroxywarfarin) and Correlation with INR, Warfarin and Drug Weekly Dosage in Patients under Oral Anticoagulant Therapy: A Pharmacogenetics Study
Abstract
Objectives: Warfarin oral anticoagulant therapy (OAT) requires regular and frequent drug adjustment monitored by INR. Interindividual variability, drug and diet interferences, and genetics (VKORC1 and CYP2C9) make the maintenance/reaching of stable INR a not so easy task. HPLC assessment of warfarin/enantiomers was suggested as a valid monitoring-tool along with INR, but definite results are still lacking. We evaluated possible correlations between INR, warfarin/3'-hydroxywarfarin, and drug weekly dosage aimed at searching novel alternatives to OAT monitoring. VKORC1/CYP2C9 pharmacogenetics investigation was performed to account for the known influence on warfarin homeostasis.
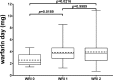
Methods: 133 OAT patients were recruited and assessed for warfarin/3'-hydroxywarfarin serum levels (HPLC), INR, and VKORC1 and CYP2C9 genotypes. A subgroup of 52 patients were monitored in detail (5 consecutive controls; c0-c4) till the target INR was reached. Correlation analyses were performed in both groups.
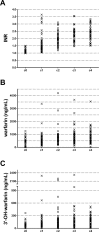
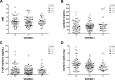
Results: In the whole OAT group both warfarin and 3'-hydroxywarfarin correlate with INR at comparable degree (r2 = 0.0388 and 0.0362 respectively). Conversely, warfarin weekly dosage better correlates with warfarin than with 3'-hydroxywarfarin (r2 = 0.0975 and r2 = 0.0381 respectively), but considering together warfarin plus 3'-hydroxywarfarin the correlation strongly increased (r2 = 0.1114; p<0.0001). Interestingly, 3'-hydroxywarfarin reached a strong correlation at c4 respect to warfarin (r2 = 0.2157 and r2 = 0.0549; p = 0.0005 and p = 0.0944 respectively) seeming less affected by drug adjustments in the subgroup of 52 patients who started OAT. The multivariate analyses aimed at estimating the true contribution of 3'-hydroxywarfarin on INR value ascribed it the unique significant value (p = 0.0021) in spite of warfarin who lost association. The pharmacogenetics studies confirmed that patients carrying the VKORC1 variant-allele required lower warfarin maintenance dosage and that the combination of VKORC1 and CYP2C9 yielded a warfarin responsive index (WRI) inversely related to the number variant alleles.
Conclusion: Our results overall suggest that 3'-hydroxywarfarin monitoring could be of great advantage in INR monitoring respect to classical warfarin assessment showing significant contribution also in multivariate analysis. Therefore, additional active metabolites should be recognized and investigated as novel useful indicators.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Ageno W, Gallus AS, Wittkowsky A, Crowther M, Hylek EM, Palareti G, et al. Oral anticoagulant therapy: Antithrombotic Therapy and Prevention of Thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest. 2012;141(2 Suppl):e44S–88S. 10.1378/chest.11-2292 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Timson DJ. Dicoumarol: a drug which hits at least two very different targets in vitamin K metabolism. Current drug targets. 2015. . - PubMed
-
- Whitlon DS, Sadowski JA, Suttie JW. Mechanism of coumarin action: significance of vitamin K epoxide reductase inhibition. Biochemistry. 1978;17(8):1371–7. . - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

