Induction of Pulmonary Granuloma Formation by Propionibacterium acnes Is Regulated by MyD88 and Nox2
- PMID: 27607191
- PMCID: PMC5248957
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2016-0035OC
Induction of Pulmonary Granuloma Formation by Propionibacterium acnes Is Regulated by MyD88 and Nox2
Abstract
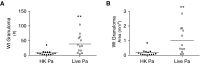
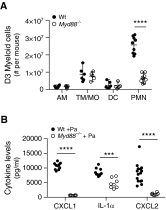
Sarcoidosis is characterized by noncaseating granulomas with an unknown cause that present primarily in the lung. Propionibacterium acnes, an immunogenic commensal skin bacterium involved in acne vulgaris, has been implicated as a possible causative agent of sarcoidosis. Here, we demonstrate that a viable strain of P. acnes isolated from a patient with sarcoidosis and instilled intratracheally into wild-type mice can generate pulmonary granulomas similar to those observed in patients with sarcoidosis. The formation of these granulomas is dependent on the administration of viable P. acnes. We also found that mice deficient in the innate immunity adapter protein MyD88 had a greater number and a larger area of granuloma lesions compared with wild-type mice administered P. acnes. Early after P. acnes administration, wild-type mice produced proinflammatory mediators and recruited neutrophils into the lung, a response that is dependent on MyD88. In addition, there was an increase in granuloma number and size after instillation with P. acnes in mice deficient in CybB, a critical component of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase required for the production of reactive oxygen species in the phagosome. Myd88-/- or Cybb-/- mice both had increased persistence of P. acnes in the lung, together with enhanced granuloma formation. In conclusion, we have generated a mouse model of early granuloma formation induced by a clinically relevant strain of P. acnes isolated from a patient with sarcoidosis, and, using this model, we have shown that a deficiency in MyD88 or CybB is associated with impaired bacterial clearance and increased granuloma formation in the lung.
Keywords: Propionibacterium acnes; granulomas; sarcoidosis.
Figures




References
-
- Statement on sarcoidosis. Joint Statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS), the European Respiratory Society (ERS) and the World Association of Sarcoidosis and Other Granulomatous Disorders (WASOG) adopted by the ATS Board of Directors and by the ERS Executive Committee, February 1999. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1999;160:736–755. - PubMed
-
- Abe C, Iwai K, Mikami R, Hosoda Y. Frequent isolation of Propionibacterium acnes from sarcoidosis lymph nodes. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1984;256:541–547. - PubMed
-
- Furusawa H, Suzuki Y, Miyazaki Y, Inase N, Eishi Y. Th1 and Th17 immune responses to viable Propionibacterium acnes in patients with sarcoidosis. Respir Investig. 2012;50:104–109. - PubMed
-
- Belkaid Y, Segre JA. Dialogue between skin microbiota and immunity. Science. 2014;346:954–959. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

