Single-Step Fabrication of Computationally Designed Microneedles by Continuous Liquid Interface Production
- PMID: 27607247
- PMCID: PMC5015976
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0162518
Single-Step Fabrication of Computationally Designed Microneedles by Continuous Liquid Interface Production
Abstract
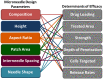
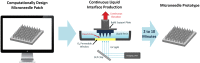
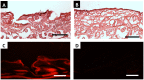
Microneedles, arrays of micron-sized needles that painlessly puncture the skin, enable transdermal delivery of medications that are difficult to deliver using more traditional routes. Many important design parameters, such as microneedle size, shape, spacing, and composition, are known to influence efficacy, but are notoriously difficult to alter due to the complex nature of microfabrication techniques. Herein, we utilize a novel additive manufacturing ("3D printing") technique called Continuous Liquid Interface Production (CLIP) to rapidly prototype sharp microneedles with tuneable geometries (size, shape, aspect ratio, spacing). This technology allows for mold-independent, one-step manufacturing of microneedle arrays of virtually any design in less than 10 minutes per patch. Square pyramidal CLIP microneedles composed of trimethylolpropane triacrylate, polyacrylic acid and photopolymerizable derivatives of polyethylene glycol and polycaprolactone were fabricated to demonstrate the range of materials that can be utilized within this platform for encapsulating and controlling the release of therapeutics. These CLIP microneedles effectively pierced murine skin ex vivo and released the fluorescent drug surrogate rhodamine.
Conflict of interest statement
I have read the journal's policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests: JRT, DS, AE, and JMD all have an equity stake in Carbon, Inc., which is a venture-backed startup company. This does not alter our adherence to PLOS One policies on data sharing and materials.
Figures





References
-
- Prausnitz MR. Microneedles for transdermal drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2004; 56:581–587. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

