Oxidized Lipoprotein Uptake Through the CD36 Receptor Activates the NLRP3 Inflammasome in Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells
- PMID: 27607416
- PMCID: PMC5024668
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.15-18663
Oxidized Lipoprotein Uptake Through the CD36 Receptor Activates the NLRP3 Inflammasome in Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells
Abstract
Purpose: Accumulation of oxidized phospholipids/lipoproteins with age is suggested to contribute to the pathogenesis of AMD. We investigated the effect of oxidized LDL (ox-LDL) on human RPE cells.
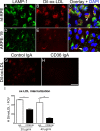
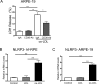
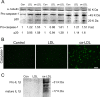
Methods: Primary human fetal RPE (hf-RPE) and ARPE-19 cells were treated with different doses of LDL or ox-LDL. Assessment of cell death was measured by lactate dehydrogenase release into the conditioned media. Barrier function of RPE was assayed by measuring transepithelial resistance. Lysosomal accumulation of ox-LDL was determined by immunostaining. Expression of CD36 was determined by RT-PCR; protein blot and function was examined by receptor blocking. NLRP3 inflammasome activation was assessed by RT-PCR, protein blot, caspase-1 fluorescent probe assay, and inhibitor assays.
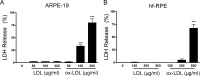
Results: Treatment with ox-LDL, but not LDL, for 48 hours caused significant increase in hf-RPE and ARPE-19 (P < 0.001) cell death. Oxidized LDL treatment of hf-RPE cells resulted in a significant decrease in transepithelial resistance (P < 0.001 at 24 hours and P < 0.01 at 48 hours) relative to LDL-treated and control cells. Internalized ox-LDL was targeted to RPE lysosomes. Uptake of ox-LDL but not LDL significantly increased CD36 protein and mRNA levels by more than 2-fold. Reverse transcription PCR, protein blot, and caspase-1 fluorescent probe assay revealed that ox-LDL treatment induced NLRP3 inflammasome when compared with LDL treatment and control. Inhibition of NLRP3 activation using 10 μM isoliquiritigenin significantly (P < 0.001) inhibited ox-LDL induced cytotoxicity.
Conclusions: These data are consistent with the concept that ox-LDL play a role in the pathogenesis of AMD by NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Suppression of NLRP3 inflammasome activation could attenuate RPE degeneration and AMD progression.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Retinal Pigment Epithelium Cell Death Is Associated With NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation by All-trans Retinal.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019 Jul 1;60(8):3034-3045. doi: 10.1167/iovs.18-26360. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019. PMID: 31311035
-
TRIM31 inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome and pyroptosis of retinal pigment epithelial cells through ubiquitination of NLRP3.Cell Biol Int. 2020 Nov;44(11):2213-2219. doi: 10.1002/cbin.11429. Epub 2020 Aug 5. Cell Biol Int. 2020. PMID: 32716108
-
NLRP3 inflammasome activation in retinal pigment epithelial cells by lysosomal destabilization: implications for age-related macular degeneration.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013 Jan 7;54(1):110-20. doi: 10.1167/iovs.12-10655. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2013. PMID: 23221073 Free PMC article.
-
NLRP3 inflammasome: activation and regulation in age-related macular degeneration.Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:690243. doi: 10.1155/2015/690243. Epub 2015 Jan 27. Mediators Inflamm. 2015. PMID: 25698849 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autophagy in dry AMD: A promising therapeutic strategy for retinal pigment epithelial cell damage.Exp Eye Res. 2024 May;242:109889. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2024.109889. Epub 2024 Apr 7. Exp Eye Res. 2024. PMID: 38593971 Review.
Cited by
-
EMT and EndMT: Emerging Roles in Age-Related Macular Degeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 16;21(12):4271. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124271. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32560057 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetics in age-related macular degeneration: new discoveries and future perspectives.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020 Mar;77(5):807-818. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03421-w. Epub 2020 Jan 2. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 31897542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early Transcriptomic Response to OxLDL in Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 21;21(22):8818. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228818. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33233417 Free PMC article.
-
Directional ABCA1-mediated cholesterol efflux and apoB-lipoprotein secretion in the retinal pigment epithelium.J Lipid Res. 2018 Oct;59(10):1927-1939. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M087361. Epub 2018 Aug 3. J Lipid Res. 2018. PMID: 30076206 Free PMC article.
-
CD36-Mediated Lipid Accumulation and Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasome Lead to Podocyte Injury in Obesity-Related Glomerulopathy.Mediators Inflamm. 2019 Apr 11;2019:3172647. doi: 10.1155/2019/3172647. eCollection 2019. Mediators Inflamm. 2019. PMID: 31097920 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Strowig T,, Henao-Mejia J,, Elinav E,, Flavell R. Inflammasomes in health and disease. 2012; 481: 278–286. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

