Acute Ethanol Increases IGF-I-Induced Phosphorylation of ERKs by Enhancing Recruitment of p52-Shc to the Grb2/Shc Complex
- PMID: 27607558
- PMCID: PMC5381968
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.25586
Acute Ethanol Increases IGF-I-Induced Phosphorylation of ERKs by Enhancing Recruitment of p52-Shc to the Grb2/Shc Complex
Abstract
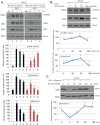
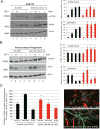
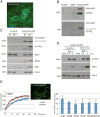
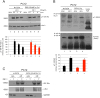
Ethanol plays a detrimental role in the development of the brain. Multiple studies have shown that ethanol inhibits insulin-like growth factor I receptor (IGF-IR) function. Because the IGF-IR contributes to brain development by supporting neural growth, survival, and differentiation, we sought to determine the molecular mechanism(s) involved in ethanol's effects on this membrane-associated tyrosine kinase. Using multiple neuronal cell types, we performed Western blot, immunoprecipitation, and GST-pulldowns following acute (1-24 h) or chronic (3 weeks) treatment with ethanol. Surprisingly, exposure of multiple neuronal cell types to acute (up to 24 h) ethanol (50 mM) enhanced IGF-I-induced phosphorylation of extracellular regulated kinases (ERKs), without affecting IGF-IR tyrosine phosphorylation itself, or Akt phosphorylation. This acute increase in ERKs phosphorylation was followed by the expected inhibition of the IGF-IR signaling following 3-week ethanol exposure. We then expressed a GFP-tagged IGF-IR construct in PC12 cells and used them to perform fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) analysis. Using these fluorescently labeled cells, we determined that 50 mM ethanol decreased the half-time of the IGF-IR-associated FRAP, which implied that cell membrane-associated signaling events could be affected. Indeed, co-immunoprecipitation and GST-pulldown studies demonstrated that the acute ethanol exposure increased the recruitment of p52-Shc to the Grb2-Shc complex, which is known to engage the Ras-Raf-ERKs pathway following IGF-1 stimulation. These experiments indicate that even a short and low-dose exposure to ethanol may dysregulate function of the receptor, which plays a critical role in brain development. J. Cell. Physiol. 232: 1275-1286, 2017. © 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
© 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors of this work have any conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Insulin receptor substrate 2 and Shc play different roles in insulin-like growth factor I signaling.J Biol Chem. 1998 Dec 18;273(51):34543-50. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.51.34543. J Biol Chem. 1998. PMID: 9852124
-
Tamoxifen interferes with the insulin-like growth factor I receptor (IGF-IR) signaling pathway in breast cancer cells.Cancer Res. 1997 Jul 1;57(13):2606-10. Cancer Res. 1997. PMID: 9205064
-
p66shc negatively regulates insulin-like growth factor I signal transduction via inhibition of p52shc binding to Src homology 2 domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase substrate-1 leading to impaired growth factor receptor-bound protein-2 membrane recruitment.Mol Endocrinol. 2008 Sep;22(9):2162-75. doi: 10.1210/me.2008-0079. Epub 2008 Jul 7. Mol Endocrinol. 2008. PMID: 18606861 Free PMC article.
-
IGF1 receptor signaling pathways.J Mol Endocrinol. 2018 Jul;61(1):T69-T86. doi: 10.1530/JME-17-0311. Epub 2018 Mar 13. J Mol Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 29535161 Review.
-
Role of the integrin alphaVbeta3 in mediating increased smooth muscle cell responsiveness to IGF-I in response to hyperglycemic stress.Growth Horm IGF Res. 2007 Aug;17(4):265-70. doi: 10.1016/j.ghir.2007.01.004. Epub 2007 Apr 6. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2007. PMID: 17412627 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Primary cilia safeguard cortical neurons in neonatal mouse forebrain from environmental stress-induced dendritic degeneration.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Jan 5;118(1):e2012482118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2012482118. Epub 2020 Dec 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33443207 Free PMC article.
-
The Placenta as a Target for Alcohol During Pregnancy: The Close Relation with IGFs Signaling Pathway.Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2021;180:119-153. doi: 10.1007/112_2021_58. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34159446 Review.
References
-
- Aberg MA, Aberg ND, Palmer TD, Alborn AM, Carlsson-Skwirut C, Bang P, Rosengren LE, Olsson T, Gage FH, Eriksson PS. IGF-I has a direct proliferative effect in adult hippocampal progenitor cells. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2003a;24:23–40. - PubMed
-
- Aberg ND, Blomstrand F, Aberg MA, Bjorklund U, Carlsson B, Carlsson-Skwirut C, Bang P, Ronnback L, Eriksson PS. Insulin-like growth factor-I increases astrocyte intercellular gap junctional communication and connexin43 expression in vitro. J Neurosci Res. 2003b;74:12–22. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

