Ret is essential to mediate GDNF's neuroprotective and neuroregenerative effect in a Parkinson disease mouse model
- PMID: 27607574
- PMCID: PMC5059866
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2016.263
Ret is essential to mediate GDNF's neuroprotective and neuroregenerative effect in a Parkinson disease mouse model
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Ret is essential to mediate GDNF's neuroprotective and neuroregenerative effect in a Parkinson disease mouse model.Cell Death Dis. 2018 May 25;9(6):634. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0636-4. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 29802278 Free PMC article.
Abstract
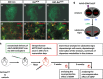
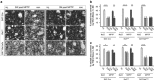
Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) is a potent survival and regeneration-promoting factor for dopaminergic neurons in cell and animal models of Parkinson disease (PD). GDNF is currently tested in clinical trials on PD patients with so far inconclusive results. The receptor tyrosine kinase Ret is the canonical GDNF receptor, but several alternative GDNF receptors have been proposed, raising the question of which signaling receptor mediates here the beneficial GDNF effects. To address this question we overexpressed GDNF in the striatum of mice deficient for Ret in dopaminergic neurons and subsequently challenged these mice with 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP). Strikingly, in this established PD mouse model, the absence of Ret completely abolished GDNF's neuroprotective and regenerative effect on the midbrain dopaminergic system. This establishes Ret signaling as absolutely required for GDNF's effects to prevent and compensate dopaminergic system degeneration and suggests Ret activation as the primary target of GDNF therapy in PD.
Figures

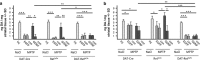
References
-
- Airaksinen MS, Saarma M. The GDNF family: signalling, biological functions and therapeutic value. Nat Rev Neurosci 2002; 3: 383–394. - PubMed
-
- Paratcha G, Ledda F. GDNF and GFRalpha: a versatile molecular complex for developing neurons. Trends Neurosci 2008; 31: 384–391. - PubMed
-
- Manfredsson FP, Okun MS, Mandel RJ. Gene therapy for neurological disorders: challenges and future prospects for the use of growth factors for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Curr Gene Ther 2009; 9: 375–388. - PubMed
-
- Aron L, Klein R. Repairing the parkinsonian brain with neurotrophic factors. Trends Neurosci 2011; 34: 88–100. - PubMed
-
- Kramer ER, Liss B. GDNF-Ret signaling in midbrain dopaminergic neurons and its implication for Parkinson disease. FEBS Lett 2015; 589: 3760–3772. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

