Inhibition of BET bromodomain-dependent XIAP and FLIP expression sensitizes KRAS-mutated NSCLC to pro-apoptotic agents
- PMID: 27607580
- PMCID: PMC5059870
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2016.271
Inhibition of BET bromodomain-dependent XIAP and FLIP expression sensitizes KRAS-mutated NSCLC to pro-apoptotic agents
Abstract
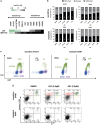
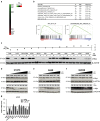
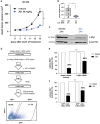
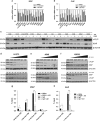
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has the highest incidence of cancer-related death worldwide and a high medical need for more effective therapies. Small-molecule inhibitors of the bromodomain and extra terminal domain (BET) family such as JQ1, I-BET762 and OTX-015 are active in a wide range of different cancer types, including lung cancer. Although their activity on oncogene expression such as c-Myc has been addressed in many studies, the effects of BET inhibition on the apoptotic pathway remain largely unknown. Here we evaluated the activity of BET bromodomain inhibitors on cell cycle distribution and on components of the apoptosis response. Using a panel of 12 KRAS-mutated NSCLC models, we found that cell lines responsive to BET inhibitors underwent apoptosis and reduced their S-phase population, concomitant with downregulation of c-Myc expression. Conversely, ectopic c-Myc overexpression rescued the anti-proliferative effect of JQ1. In the H1373 xenograft model, treatment with JQ1 significantly reduced tumor growth and downregulated the expression of c-Myc. The effects of BET inhibition on the expression of 370 genes involved in apoptosis were compared in sensitive and resistant cells and we found the expression of the two key apoptosis regulators FLIP and XIAP to be highly BET dependent. Consistent with this, combination treatment of JQ1 with the tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) or the pro-apoptotic chemotherapeutic agent cisplatin enhanced induction of apoptosis in both BET inhibitor sensitive and resistant cells. Further we showed that combination of JQ1 with cisplatin led to significantly improved anti-tumor efficacy in A549 tumor-bearing mice. Altogether, these results show that the identification of BET-dependent genes provides guidance for the choice of drug combinations in cancer treatment. They also demonstrate that BET inhibition primes NSCLC cells for induction of apoptosis and that a combination with pro-apoptotic compounds represents a valuable strategy to overcome treatment resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
OK, RL, KAG, BH and PL are employees of Bayer Pharma AG, a company having a commercial interest in the development of BET inhibitors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Efficacy of BET bromodomain inhibition in Kras-mutant non-small cell lung cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Nov 15;19(22):6183-92. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-3904. Epub 2013 Sep 17. Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 24045185 Free PMC article.
-
KRAS-mutation status dependent effect of zoledronic acid in human non-small cell cancer preclinical models.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 29;7(48):79503-79514. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12806. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27780929 Free PMC article.
-
The BET bromodomain inhibitor, JQ1, facilitates c-FLIP degradation and enhances TRAIL-induced apoptosis independent of BRD4 and c-Myc inhibition.Oncotarget. 2015 Oct 27;6(33):34669-79. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5785. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26415225 Free PMC article.
-
The improbable targeted therapy: KRAS as an emerging target in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Cell Rep Med. 2021 Jan 19;2(1):100186. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2020.100186. eCollection 2021 Jan 19. Cell Rep Med. 2021. PMID: 33521700 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BET bromodomain inhibitors--a novel epigenetic approach in castration-resistant prostate cancer.Cancer Biol Ther. 2014;15(12):1583-5. doi: 10.4161/15384047.2014.962297. Cancer Biol Ther. 2014. PMID: 25535892 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Super-enhancers: a new frontier for epigenetic modifiers in cancer chemoresistance.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 May 19;40(1):174. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-01974-y. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34011395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of programmed cell death by Brd4.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Dec 20;13(12):1059. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05505-1. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 36539410 Free PMC article. Review.
-
JQ1 affects BRD2-dependent and independent transcription regulation without disrupting H4-hyperacetylated chromatin states.Epigenetics. 2018;13(4):410-431. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2018.1469891. Epub 2018 Aug 6. Epigenetics. 2018. PMID: 30080437 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of Long Noncoding RNA ENST457720 Inhibits Proliferation of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells In Vitro and In Vivo.Oncol Res. 2018 Dec 27;27(1):47-53. doi: 10.3727/096504018X15193843443255. Epub 2018 Mar 1. Oncol Res. 2018. PMID: 29495976 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Roles of Bromodomain Proteins in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jul 19;13(14):3606. doi: 10.3390/cancers13143606. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34298819 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

