A Review on the Terpenes from Genus Vitex
- PMID: 27608002
- PMCID: PMC6273030
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules21091179
A Review on the Terpenes from Genus Vitex
Abstract
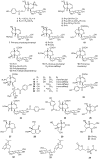
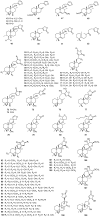
The genus Vitex, which belongs to the Verbenaceae family, includes approximately 250 species. Some species of the genus Vitex have traditionally been used for the treatment of headaches, ophthalmodynia, coughs, asthma, premenopausal syndrome, etc. Chemical investigations indicate that the characteristic constituents of the genus Vitex are terpenes, and 210 of these compounds, including monoterpenoids, sesquiterpenoids, diterpenoids and triterpenoids, have been obtained from 12 species. Pharmacological studies had shown that these terpenes possess anti-inflammatory, antitumor, antibacterial, antioxidant activities, and so on. In this paper, the identity of these terpenes and their pharmacological effects are reviewed, which can provide references for further research regarding the chemistry and utilization of the Vitex species.
Keywords: Vitex genus; chemical constituents; pharmacological effects; terpenes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Pei J., Chen S.L. Flora of China. Science Press; Beijing, China: 1982.
-
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission . Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China. Beijing Chemical Industry Press; Beijing, China: 2015.
-
- Li C.Z., Su Y.F., Jin X.J. Advances in studies on chemical constituents from plants of Vitex L. and their bioactivities. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs. 2005;36:930–938.
-
- Wu C., Zhang J., Yin Z.Q. Chemical constituents from the fruits of Vitex rotundifolia. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2010;17:504–507.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

