Plasma exosome microRNAs are indicative of breast cancer
- PMID: 27608715
- PMCID: PMC5016889
- DOI: 10.1186/s13058-016-0753-x
Plasma exosome microRNAs are indicative of breast cancer
Abstract
Background: microRNAs are promising candidate breast cancer biomarkers due to their cancer-specific expression profiles. However, efforts to develop circulating breast cancer biomarkers are challenged by the heterogeneity of microRNAs in the blood. To overcome this challenge, we aimed to develop a molecular profile of microRNAs specifically secreted from breast cancer cells. Our first step towards this direction relates to capturing and analyzing the contents of exosomes, which are small secretory vesicles that selectively encapsulate microRNAs indicative of their cell of origin. To our knowledge, circulating exosome microRNAs have not been well-evaluated as biomarkers for breast cancer diagnosis or monitoring.
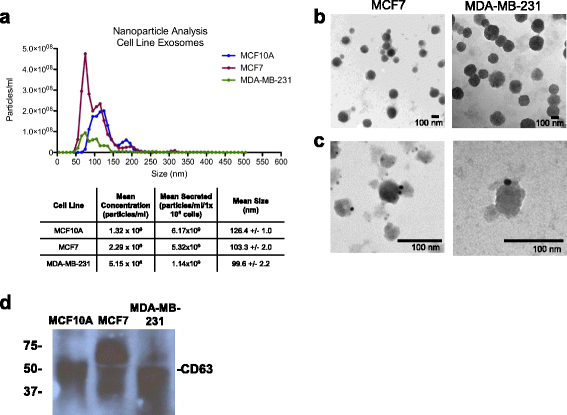
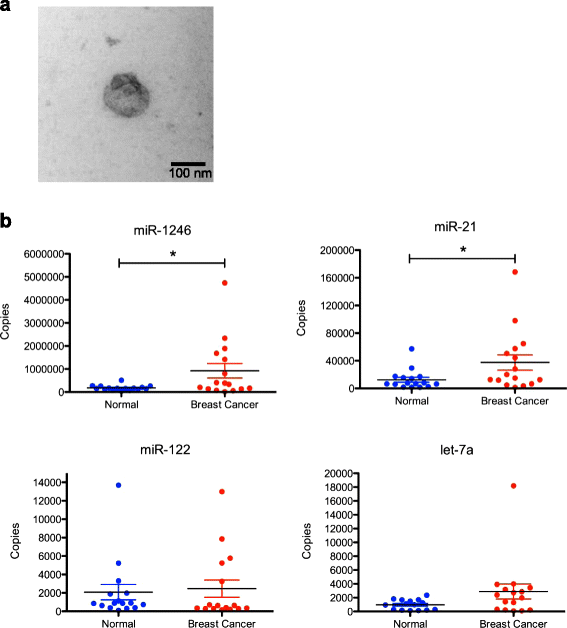
Methods: Exosomes were collected from the conditioned media of human breast cancer cell lines, mouse plasma of patient-derived orthotopic xenograft models (PDX), and human plasma samples. Exosomes were verified by electron microscopy, nanoparticle tracking analysis, and western blot. Cellular and exosome microRNAs from breast cancer cell lines were profiled by next-generation small RNA sequencing. Plasma exosome microRNA expression was analyzed by qRT-PCR analysis.
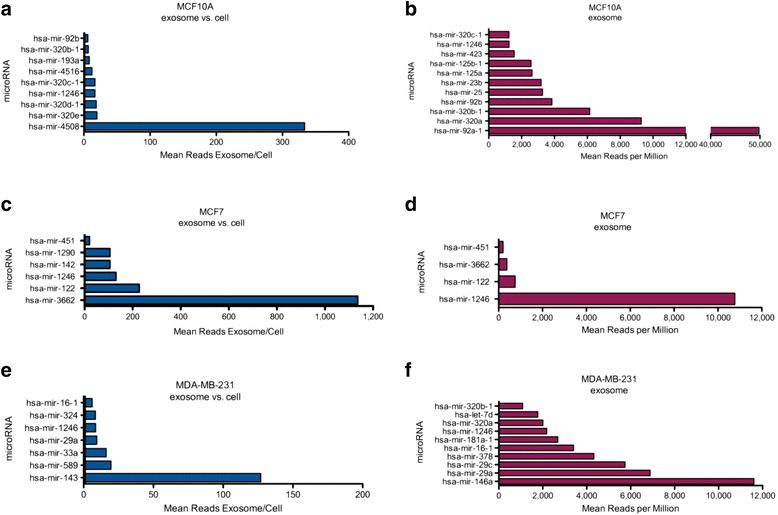
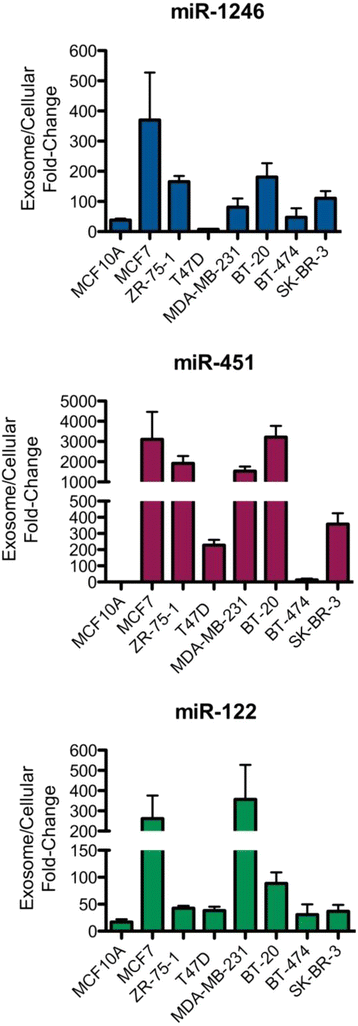
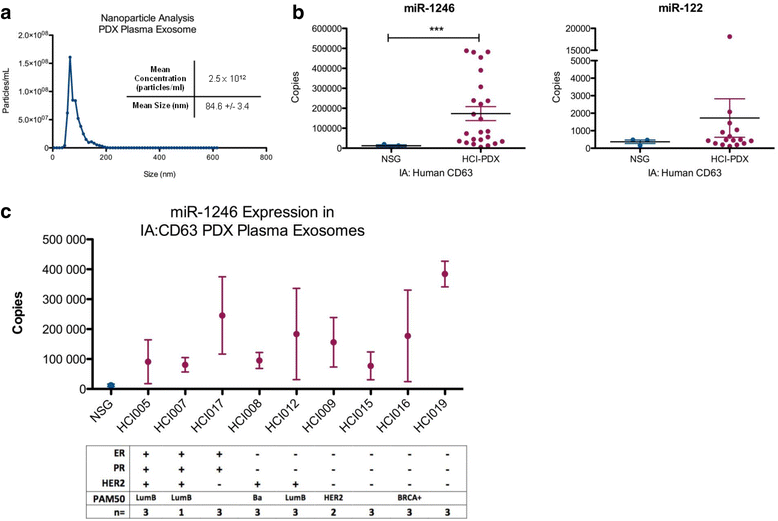
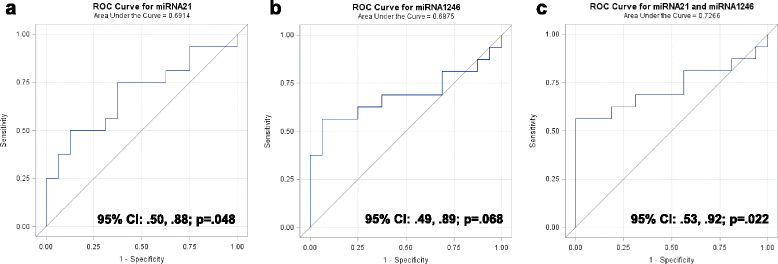
Results: Small RNA sequencing and qRT-PCR analysis showed that several microRNAs are selectively encapsulated or highly enriched in breast cancer exosomes. Importantly, the selectively enriched exosome microRNA, human miR-1246, was detected at significantly higher levels in exosomes isolated from PDX mouse plasma, indicating that tumor exosome microRNAs are released into the circulation and can serve as plasma biomarkers for breast cancer. This observation was extended to human plasma samples where miR-1246 and miR-21 were detected at significantly higher levels in the plasma exosomes of 16 patients with breast cancer as compared to the plasma exosomes of healthy control subjects. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis indicated that the combination of plasma exosome miR-1246 and miR-21 is a better indicator of breast cancer than their individual levels.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate that certain microRNA species, such as miR-21 and miR-1246, are selectively enriched in human breast cancer exosomes and significantly elevated in the plasma of patients with breast cancer. These findings indicate a potential new strategy to selectively analyze plasma breast cancer microRNAs indicative of the presence of breast cancer.
Keywords: Biomarker; Breast cancer; Exosomes; Patient-derived xenograft; microRNA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Exosome-mediated transfer of miR-10b promotes cell invasion in breast cancer.Mol Cancer. 2014 Nov 26;13:256. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-256. Mol Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25428807 Free PMC article.
-
Exosome-mediated microRNA signaling from breast cancer cells is altered by the anti-angiogenesis agent docosahexaenoic acid (DHA).Mol Cancer. 2015 Jul 16;14:133. doi: 10.1186/s12943-015-0400-7. Mol Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26178901 Free PMC article.
-
Increased number of circulating exosomes and their microRNA cargos are potential novel biomarkers in alcoholic hepatitis.J Transl Med. 2015 Aug 12;13:261. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0623-9. J Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 26264599 Free PMC article.
-
Exosome-encapsulated microRNAs as circulating biomarkers for breast cancer.Int J Cancer. 2016 Oct 1;139(7):1443-8. doi: 10.1002/ijc.30179. Epub 2016 May 31. Int J Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27170104 Review.
-
Effect of exosome biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of breast cancer patients.Clin Transl Oncol. 2018 Jul;20(7):906-911. doi: 10.1007/s12094-017-1805-0. Epub 2017 Nov 15. Clin Transl Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29143228
Cited by
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Regenerative Potential and Challenges.Biology (Basel). 2021 Feb 25;10(3):172. doi: 10.3390/biology10030172. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33668707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-1246 Targets CCNG2 to Enhance Cancer Stemness and Chemoresistance in Oral Carcinomas.Cancers (Basel). 2018 Aug 16;10(8):272. doi: 10.3390/cancers10080272. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30115848 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-derived exosomes in cancer metastasis risk diagnosis and metastasis therapy.Clin Transl Oncol. 2019 Feb;21(2):152-159. doi: 10.1007/s12094-018-1918-0. Epub 2018 Jul 26. Clin Transl Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30051211 Review.
-
Validation of a Patient-Derived Xenograft Model for Cervical Cancer Based on Genomic and Phenotypic Characterization.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jun 16;14(12):2969. doi: 10.3390/cancers14122969. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35740635 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles in cancer therapy.Semin Cancer Biol. 2022 Nov;86(Pt 2):296-309. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2022.06.001. Epub 2022 Jun 8. Semin Cancer Biol. 2022. PMID: 35688334 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Society. AC . Breast Cancer Facts & Figures 2013-2014. Atlanta: American Cancer Society, Inc; 2013.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

