GPR30 disrupts the balance of GABAergic and glutamatergic transmission in the spinal cord driving to the development of bone cancer pain
- PMID: 27608844
- PMCID: PMC5341991
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.11867
GPR30 disrupts the balance of GABAergic and glutamatergic transmission in the spinal cord driving to the development of bone cancer pain
Abstract
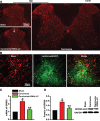
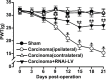
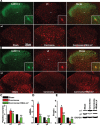
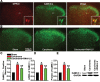
Cancer induced bone pain is a very complicated clinical pain states that has proven difficult to be treated effectively due to poorly understand of underlying mechanism, but bone cancer pain (BCP) seems to be enhanced by a state of spinal sensitization. In the present study, we showed that carcinoma tibia implantation induced notable pain sensitization and up-regulation of G-protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPR30) in the spinal cord of rats which was reversed by GPR30 knockdown. Further studies indicated that upregulation of GPR30 induced by cancer implantation resulted in a select loss of γ-aminobutyric acid-ergic (GABAergic) neurons and functionally diminished the inhibitory transmission due to reduce expression of the vesicular GABA transporter (VGAT). GPR30 contributed to spinal cord disinhibition by diminishing the inhibitory transmission via upregulation of α1 subunit and downregulation of γ2 subunits. GPR30 also facilitated excitatory transmission by promoting functional up-regulation of the calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II α (CaMKII α) in glutamatergic neurons and increasing the clustering of the glutamate receptor subunit 1 (GluR1) subunit to excitatory synapse.Taken together, GPR30 contributed to the development of BCP by both facilitating excitatory transmission and inhibiting inhibitory transmission in the spinal cord. Our findings provide the new spinal disinhibition and sensitivity mechanisms underlying the development of bone cancer pain.
Keywords: GPR30; bone cancer pain; excitatory transmission; inhibitory transmission; spinal cord.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ca2+ /calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in spinal dorsal horn contributes to the pain hypersensitivity induced by γ-aminobutyric acid type a receptor inhibition.J Neurosci Res. 2013 Nov;91(11):1473-82. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23270. Epub 2013 Aug 23. J Neurosci Res. 2013. PMID: 24038144
-
Estrogen receptor GPR30 exerts anxiolytic effects by maintaining the balance between GABAergic and glutamatergic transmission in the basolateral amygdala of ovariectomized mice after stress.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2013 Oct;38(10):2218-33. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2013.04.011. Epub 2013 May 11. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2013. PMID: 23669322
-
Protocadherin20 promotes excitatory synaptogenesis in dorsal horn and contributes to bone cancer pain.Neuropharmacology. 2013 Dec;75:181-90. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.07.010. Epub 2013 Aug 2. Neuropharmacology. 2013. PMID: 23911744
-
Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Calcium/Calmodulin-Dependent Protein Kinase II in Chronic Pain.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2017 Nov;363(2):176-183. doi: 10.1124/jpet.117.243048. Epub 2017 Aug 30. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2017. PMID: 28855373 Review.
-
Understanding the initiation, delivery and processing of bone cancer pain from the peripheral to the central nervous system.Neuropharmacology. 2023 Oct 1;237:109641. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2023.109641. Epub 2023 Jun 29. Neuropharmacology. 2023. PMID: 37392821 Review.
Cited by
-
GPR30-mediated estrogenic regulation of actin polymerization and spatial memory involves SRC-1 and PI3K-mTORC2 in the hippocampus of female mice.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2019 Jun;25(6):714-733. doi: 10.1111/cns.13108. Epub 2019 Feb 3. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2019. PMID: 30714337 Free PMC article.
-
Osteoporosis in Light of a New Mechanism Theory of Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness and Non-Contact Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 12;23(16):9046. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169046. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012312 Free PMC article.
-
The Antitumor Peptide ERα17p Exerts Anti-Hyperalgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Actions Through GPER in Mice.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Mar 17;12:578250. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.578250. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33815268 Free PMC article.
-
Amitriptyline influences the mechanical withdrawal threshold in bone cancer pain rats by regulating glutamate transporter GLAST.Mol Pain. 2019 Jan-Dec;15:1744806919855834. doi: 10.1177/1744806919855834. Mol Pain. 2019. PMID: 31218920 Free PMC article.
-
G protein-coupled estrogen receptor in the rostral ventromedial medulla contributes to the chronification of postoperative pain.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2021 Nov;27(11):1313-1326. doi: 10.1111/cns.13704. Epub 2021 Jul 13. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2021. PMID: 34255932 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Donovan-Rodriguez T, Urch CE, Dickenson AH. Evidence of a role for descending serotonergic facilitation in a rat model of cancer-induced bone pain. Neuroscience Letters. 2006;393:237–42. - PubMed
-
- Mundy GR. Metastasis to bone: causes, consequences and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:584–93. - PubMed
-
- Honore P, Mantyh PW. Bone cancer pain: from mechanism to model to therapy. Pain Med. 2000;1:303–09. - PubMed
-
- Mantyh PW. Cancer pain and its impact on diagnosis, survival and quality of life. Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 2006;7:797–809. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

