HIV prevention advice for people with serious mental illness
- PMID: 27609030
- PMCID: PMC6457823
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009639.pub3
HIV prevention advice for people with serious mental illness
Abstract
Background: People with serious mental illness have rates of Human Immuno-deficiency Virus (HIV) infection higher than expected in the general population for the same demographic area. Despite this elevated prevalence, UK national strategies around sexual health and HIV prevention do not state that people with serious mental illness are a high risk group. However, a significant proportion in this group are sexually active and engage in HIV-risk behaviours including having multiple sexual partners, infrequent use of condoms and trading sex for money or drugs. Therefore we propose the provision of HIV prevention advice could enhance the physical and social well being of this population.
Objectives: To assess the effects of HIV prevention advice in reducing morbidity, mortality and preserving the quality of life in people with serious mental illness.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Schizophrenia Group's Trials Register (24 January 2012; 4 July 2016).
Selection criteria: We planned to include all randomised controlled trials focusing on HIV prevention advice versus standard care or comparing HIV prevention advice with other more focused methods of delivering care or information for people with serious mental illness.
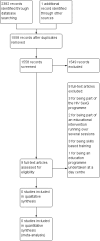
Data collection and analysis: Review authors (NW, AC, AA, GT) independently screened search results and did not identify any studies that fulfilled the review's criteria.
Main results: We did not identify any randomised studies that evaluated advice regarding HIV for people with serious mental illness. The excluded studies illustrate that randomisation of packages of care relevant to both people with serious mental illness and HIV risk are possible.
Authors' conclusions: Policy makers, clinicians, researchers and service users need to collaborate to produce guidance on how best to provide advice for people with serious mental illness in preventing the spread of HIV infection. It is entirely feasible that this could be within the context of a well-designed simple large randomised study.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Update of
References
References to studies excluded from this review
Berkman 2006 {published data only}
-
- Berkman A, Cerwonka ER, Sohler N, Susser E. A randomized trial of a brief HIV risk reduction intervention for men with severe mental. Psychiatric Services 2006;57:407‐9. - PubMed
Berkman 2007 {published data only}
-
- Berkman A, Pilowsky D, Zybert P, Herman DB, Conver S, Lemelle S, et al. HIV prevention with severely mentally ill men: A randomized controlled trial. AIDS Care 2006;19:579‐88. - PubMed
Collins 2001 {published data only}
Katz 1996 {published data only}
-
- Katz RC, Westerman C, Beauchamp K, Clay C. Effects of AIDS counseling and risk reduction training on the chronic mentally ill. AIDS Education and Prevention 1996;8(5):457‐63. - PubMed
Kelly 1997 {published data only}
-
- Kelly JA, McAuliffe TL, Sikkema KJ, Murphy DA, Somlai AM, Mulry G, et al. Reduction in risk behavior among adults with severe mental illness who learned to advocate for HIV prevention. Psychiatric Services 1997;48(10):1283‐8. - PubMed
Kern 1996a {published data only}
-
- Kern SM. Assessment of a training program for AIDS education for persons with serious mental illness. PhD Thesis. Temple University, 1996; Vol. N/A:N/A.
Otto‐Salaj 2001 {published data only}
-
- Otto‐Salaj LL, Kelly JA, Stevenson LY, Hoffmann R, Kalichman SC. Outcomes of a randomized small‐group hiv prevention intervention trial for people with serious mental illness. Community Mental Health Journal 2001;37(2):123‐44. - PubMed
Susser 1998 {published data only}
-
- Susser E, Valencia E, Berkman A, Sohler N, Conover S, Torres J, et al. Human Immunodeficiency Virus sexual risk reduction in homeless men with mental illness. Archives of General Psychiatry 1998;55:266‐72. - PubMed
Weinhardt 1998 {published data only}
-
- Weinhardt LS, Carey MP, Carey KB, Verdecias RN. Increasing assertiveness skills to reduce HIV risk among women living with a severe and persistent mental illness. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology 1998;66(4):680‐4. - PubMed
Additional references
Altman 1996
Bland 1997
Boissel 1999
-
- Boissel JP, Cucherat M, Li W, Chatellier G, Gueyffier F, Buyse M, et al. The problem of therapeutic efficacy indices. 3. Comparison of the indices and their use [Apercu sur la problematique des indices d'efficacite therapeutique, 3: comparaison des indices et utilisation. Groupe d'etude des Indices d'efficacite]. Therapie 1999;54(4):405‐11. [PUBMED: 10667106] - PubMed
Bradshaw 2005
-
- Bradshaw T, Lovell K, Harris N. Healthy living interventions and schizophrenia: a systematic review. Journal of Advanced Nursing 2005;49(6):634‐54. [PUBMED: 15737224] - PubMed
Carey 2004
Cooper 2003
-
- Cooper. Evidence‐based mental health policy: a critical appraisal. British Journal of Psychiatry 2003;183:105–13. [PUBMED: 12893663] - PubMed
Cournos 1991
-
- Cournos F, Empfield M, Horwath E, McKinnon K, Meyer I, Schrage H, et al. HIV seroprevalence among patients admitted to two psychiatric hospitals. American Journal of Psychiatry 1991;148(9):1225‐30. [PUBMED: 1883002] - PubMed
Cournos 2005
-
- Cournos F, McKinnon K, Sullivan G. Schizophrenia and comorbid human immunodeficiency virus or hepatitis C virus. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 2005;66(Suppl 6):27‐33. [PUBMED: 16107181] - PubMed
Deeks 2000
-
- Deeks J. Issues in the selection for meta‐analyses of binary data. Proceedings of the 8th International Cochrane Colloquium; 2000 Oct 25‐28; Cape town. Cape Town: The Cochrane Collaboration, 2000.
Divine 1992
-
- Divine GW, Brown JT, Frazier LM. The unit of analysis error in studies about physicians' patient care behavior. Journal of General Internal Medicine 1992;7(6):623‐9. - PubMed
Dixon 1999
-
- Dixon L, Postrado L, Delahanty J, Fischer PJ, Lehman A. The association of medical comorbidity in schizophrenia with poor physical and mental health. Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease 1999;187(8):496‐502. [PUBMED: 10463067] - PubMed
Donner 2002
-
- Donner A, Klar N. Issues in the meta‐analysis of cluster randomized trials. Statistics in Medicine 2002;21:2971‐80. - PubMed
Egger 1997
Elbourne 2002
-
- Elbourne D, Altman DG, Higgins JPT, Curtina F, Worthingtond HV, Vaile A. Meta‐analyses involving cross‐over trials: methodological issues. International Journal of Epidemiology 2002;31(1):140‐9. - PubMed
Grassi 1999
-
- Grassi L, Pavanati M, Cardelli R, Ferri S, Peron L. HIV‐risk behaviour and knowledge about HIV/AIDS among patients with schizophrenia. Psychological Medicine 1999;29(1):171‐9. [PUBMED: 10077305] - PubMed
Greenlund 2002
-
- Greenlund KJ, Giles WH, Keenan NL, Croft JB, Mensah GA. Physician advice, patient actions, and health‐related quality of life in secondary prevention of stroke through diet and exercise. Stroke 2002;33(2):565‐70. [PUBMED: 11823671] - PubMed
Gulliford 1999
-
- Gulliford MC. Components of variance and intraclass correlations for the design of community‐based surveys and intervention studies: data from the health survey for England 1994. American Journal of Epidemiology 1999;149:876‐83. - PubMed
Higgins 2003
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.2 [updated September 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Hughes 2009
-
- Hughes E, Gray R. HIV prevention for people with serious mental illness: a survey of mental health workers' attitudes, knowledge and practice. Journal of Clinical Nursing 2009;18(4):591‐600. [PUBMED: 19192006] - PubMed
Kay 1986
-
- Kay SR, Opler LA, Fiszbein A. Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) Manual. North Tonawanda, NY: Multi‐Health Systems, 1986.
Kay 1987
-
- Kay SR, Fiszbein A, Opler LA. The positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Bulletin 1987;13(2):261‐76. [PUBMED: 3616518] - PubMed
Khanna 2012
Khokhar 2011
Kreuter 2000
-
- Kreuter MW, Chheda SG, Bull FC. How does physician advice influence patient behavior? Evidence for a priming effect. Archives of Family Medicine 2000;9(5):426‐33. [PUBMED: 10810947] - PubMed
Leucht 2005
-
- Leucht S, Kane JM, Kissling W, Hamann J, Etschel E, Engel R. Clinical implications of brief psychiatric rating scale scores. British Journal of Psychiatry 2005;187:366‐71. [PUBMED: 16199797] - PubMed
Leucht 2005a
-
- Leucht S, Kane JM, Kissling W, Hamann J, Etschel E, Engel RR. What does the PANSS mean?. Schizophrenia Research 2005;79(2‐3):231‐8. [PUBMED: 15982856] - PubMed
Marshall 2000
-
- Marshall M, Lockwood A, Bradley C, Adams C, Joy C, Fenton M. Unpublished rating scales: a major source of bias in randomised controlled trials of treatments for schizophrenia. British Journal of Psychiatry 2000;176:249‐52. [PUBMED: 10755072] - PubMed
NAPWA 2012
-
- National Association of People living With HIV/AIDS. A CHECKLIST GUIDEFOR PEOPLE WITH HIV. http://www.napwa.org.au/files/checklist%20guide%202012%20webversion.pdf. Newtown NSW 2042 Australia: National Association of People living With HIV/AIDS, 2012.
NIMH 1987
-
- National Institute of Mental Health. Towards a Model for a Comprehensive Community‐Based Mental Health System. National Institute of Mental Health Washington, DC: NIMH, 1987.
OED
-
- OED Oxford English Dictionary. Oxford English Dictionary: The Definitive Record of the English Language. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2013.
Overall 1962
-
- Overall JE, Gorham DR. The brief psychiatric rating scale. Psychological Reports 1962;10:799‐812.
Robson 2007
-
- Robson D, Gray R. Serious mental illness and physical health problems: a discussion paper. International Journal of Nursing Studies 2007;44(3):457‐66. [PUBMED: 17007859] - PubMed
Rosenberg 2001
Ruggeri 2000
-
- Ruggeri M, Leese M, Thornicroft G, Bisoffi G, Tansella M. Definition and prevalence of severe and persistent mental illness. British Journal of Psychiatry 2000;177:149‐55. [PUBMED: 11026955] - PubMed
Russell 1979
Schinnar 1990
-
- Schinnar AP, Rothbard AB, Kanter R, Jung YS. An empirical literature review of definitions of severe and persistent mental illness. American Journal of Psychiatry 1990;147(12):1602‐8. [PUBMED: 2244636] - PubMed
Stott 1990
-
- Stott NC, Pill RM. 'Advise yes, dictate no'. Patients' views on health promotion in the consultation. Family Practice 1990;7(2):125‐31. [PUBMED: 2369980] - PubMed
Susser 1993
Susser 1994
-
- Susser E, Torres J. Sex, games, and videotapes: an HIV prevention for men who are homeless and mentally ill. Psychosocial Rehabilitation Journal 1994;17:31‐40.
Sutherland 2003
Tanenbaum 2005
-
- Tanenbaum. Evidence‐based practice as mental health policy: Three controversies and a caveat. Health Affairs 2005;24(1):163–73. [PUBMED: 15647227] - PubMed
The Global HIV Prevention Working Group 2006
-
- The Global HIV Prevention Working Group. New approaches to HIV prevention: Accelerating research and ensuring future access. http://www.globalhivprevention.org/pdfs/New%20Prevention%20Approaches.pdf (accessed 7 February 2011).
Tosh 2010
Tosh 2011
Ukoumunne 1999
-
- Ukoumunne OC, Gulliford MC, Chinn S, Sterne JAC, Burney PGJ. Methods for evaluating area‐wide and organisation‐based intervention in health and health care: a systematic review. Health Technology Assessment 1999;3(5):1‐75. - PubMed
UNAIDS 2010
-
- UNAIDS. Global report: UNAIDS report on the global AIDS epidemic 2010. United Nations, 2010.
Xia 2009
-
- Xia J, Adams CE, Bhagat N, Bhagat V, Bhoopathi P, El‐Sayeh H, et al. Loss to outcomes stakeholder survey: the LOSS study. Psychiatric Bulletin 2009;33(7):254‐7.
Zimmerman 1994
-
- Zimmerman M. Diagnosing personality disorders. A review of issues and research methods. Archives of General Psychiatry 1994;51(3):225‐45. [PUBMED: 8122959] - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous