Pulse pressure variation shows a direct linear correlation with tidal volume in anesthetized healthy patients
- PMID: 27609188
- PMCID: PMC5017055
- DOI: 10.1186/s12871-016-0233-y
Pulse pressure variation shows a direct linear correlation with tidal volume in anesthetized healthy patients
Abstract
Background: The settings of mechanical ventilation, like tidal volume (VT), occasionally need to be adjusted in the process of anesthesia for some special reasons. The aim of this study was therefore to assess the relationship between pulse pressure variations (PPVs) in different settings of VT in anesthetized healthy patients under mechanical ventilation.
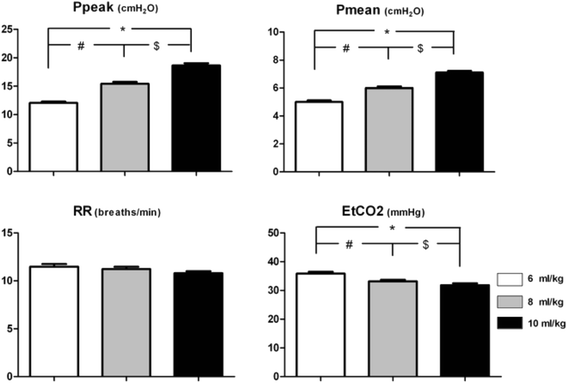
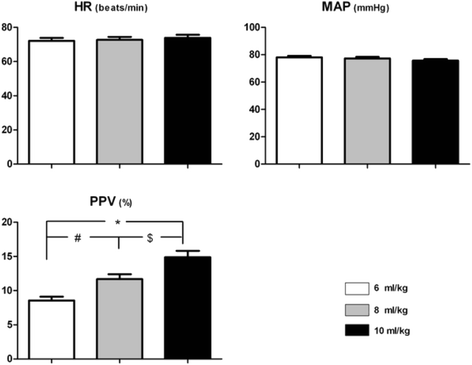
Methods: Sixty nine ASA I-II patients scheduled for gastrointestinal surgery under general anesthesia were included in this prospective study. All the patients were ventilated at a VT of 6, 8 or 10 ml/kg (predicted body weight) with no positive end expiratory pressure (PEEP) in a random order after intubation. PPV, mean arterial blood pressure, and other hemodynamic and respiratory parameters were recorded in each VT setting respectively after Partial Pressure of End-Tidal Expiration Carbon Dioxide (PetCO2) maintained between 30 mmHg and 40 mmHg by changing Respiratory Rate (RR) before incision.
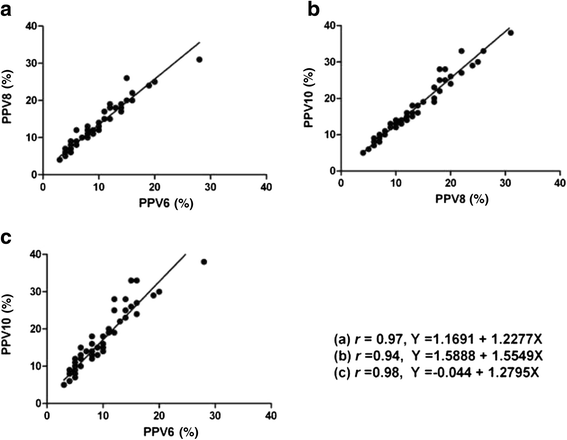
Results: The values of PPV at different settings of VT showed a tight correlation between each other (6 vs. 8 ml/kg: r = 0.97, P < 0.0001; 6 vs.10 ml/kg: r = 0.95, P < 0.0001; 8 vs. 10 ml/kg: r = 0.98, P < 0.0001, respectively).
Conclusion: There is a direct linear correlation between PPVs at different tidal volumes in anesthetized ASA I-II patients. PPV in any of the 3 VT settings (6, 8 or 10 ml/kg) can deduce that in any other 2 settings. Further studies are needed to explore the effect of intraoperative confounders for this knowledge to be clinically applied.
Trial registration: NCT01950949 , www.clinicaltrials.gov , July 26, 2013.
Keywords: Blood pressure; Mechanical ventilation; Pulse pressure variation; Tidal volume; Volume.
Figures


References
-
- Wang P, Zhou M, Rana MW, Ba ZF, Chaudry IH. Differential alterations in microvascular perfusion in various organs during early and late sepsis. Am J Physiol. 1992;263(1 Pt 1):G38–43. - PubMed
-
- Bliacheriene F, Machado SB, Fonseca EB, Otsuke D, Auler JO, Jr, Michard F. Pulse pressure variation as a tool to detect hypovolaemia during pneumoperitoneum. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2007;51(9):1268–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

