Glomerular basement membrane heparan sulfate in health and disease: A regulator of local complement activation
- PMID: 27609404
- PMCID: PMC5026315
- DOI: 10.1016/j.matbio.2016.09.002
Glomerular basement membrane heparan sulfate in health and disease: A regulator of local complement activation
Abstract
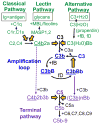
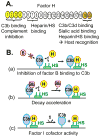
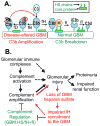
The glomerular basement membrane (GBM) is an essential component of the glomerular filtration barrier. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans such as agrin are major components of the GBM, along with α345(IV) collagen, laminin-521 and nidogen. A loss of GBM heparan sulfate chains is associated with proteinuria in several glomerular diseases and may contribute to the underlying pathology. As the major determinants of the anionic charge of the GBM, heparan sulfate chains have been thought to impart charge selectivity to the glomerular filtration, a view challenged by the negligible albuminuria in mice that lack heparan sulfate in the GBM. Recent studies provide increasing evidence that heparan sulfate chains modulate local complement activation by recruiting complement regulatory protein factor H, the major inhibitor of the alternative pathway in plasma. Factor H selectively inactivates C3b bound to surfaces bearing host-specific polyanions such as heparan sulfate, thus limiting complement activation on self surfaces such as the GBM, which are not protected by cell-bound complement regulators. We discuss mechanisms whereby the acquired loss of GBM heparan sulfate can impair the local regulation of the alternative pathway, exacerbating complement activation and glomerular injury in immune-mediated kidney diseases such as membranous nephropathy and lupus nephritis.
Keywords: Alternative pathway; Complement; Factor H; Glomerular basement membrane; Heparan sulfate.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- St John PL, Abrahamson DR. Glomerular endothelial cells and podocytes jointly synthesize laminin-1 and -11 chains. Kidney Int. 2001;60(3):1037–46. - PubMed
-
- Barker DF, Hostikka SL, Zhou J, Chow LT, Oliphant AR, Gerken SC, Gregory MC, Skolnick MH, Atkin CL, Tryggvason K. Identification of mutations in the COL4A5 collagen gene in Alport syndrome. Science. 1990;248(4960):1224–7. - PubMed
-
- Mochizuki T, Lemmink HH, Mariyama M, Antignac C, Gubler MC, Pirson Y, Verellen-Dumoulin C, Chan B, Schroder CH, Smeets HJ, et al. Identification of mutations in the alpha 3(IV) and alpha 4(IV) collagen genes in autosomal recessive Alport syndrome. Nature genetics. 1994;8(1):77–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

