Heterozygosity for transmembrane activator and calcium modulator ligand interactor A144E causes haploinsufficiency and pneumococcal susceptibility in mice
- PMID: 27609654
- PMCID: PMC5337448
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.07.028
Heterozygosity for transmembrane activator and calcium modulator ligand interactor A144E causes haploinsufficiency and pneumococcal susceptibility in mice
Abstract
Background: The B-cell receptor transmembrane activator and calcium modulator ligand interactor (TACI) is important for T-independent antibody responses. One in 200 blood donors are heterozygous for the TACI A181E mutation.
Objective: We sought to investigate the effect on B-cell function of TACI A181E heterozygosity in reportedly healthy subjects and of the corresponding TACI A144E mutation in mice.
Methods: Nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) activation was measured by using the luciferase assay in 293T cells cotransfected with wild-type and mutant TACI. TACI-driven proliferation, isotype switching, and antibody responses were measured in B cells from heterozygous TACI A144E knock-in mice. Mouse mortality was monitored after intranasal pneumococcal challenge.
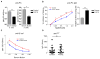
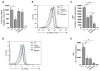
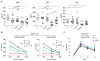
Results: Levels of natural antibodies to the pneumococcal polysaccharide component phosphocholine were significantly lower in A181E-heterozygous than TACI-sufficient Swedish blood donors never immunized with pneumococcal antigens. Although overexpressed hTACI A181E and mTACI A144E acted as dominant-negative mutations in transfectants, homozygosity for A144E in mice resulted in absent TACI expression in B cells, indicating that the mutant protein is unstable when naturally expressed. A144E heterozygous mice, such as TACI+/- mice, expressed half the normal level of TACI on their B cells and exhibited similar defects in a proliferation-inducing ligand-driven B-cell activation, antibody responses to TNP-Ficoll, production of natural antibodies to phosphocholine, and survival after intranasal pneumococcal challenge.
Conclusion: These results suggest that TACI A181E heterozygosity results in TACI haploinsufficiency with increased susceptibility to pneumococcal infection. This has important implications for asymptomatic TACI A181E carriers.
Keywords: B cells; Transmembrane activator and calcium modulator ligand interactor; common variable immunodeficiency; natural antibodies; pneumococcal susceptibility.
Copyright © 2016 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicting financial interest to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The murine equivalent of the A181E TACI mutation associated with common variable immunodeficiency severely impairs B-cell function.Blood. 2009 Sep 10;114(11):2254-62. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-11-189720. Epub 2009 Jul 15. Blood. 2009. PMID: 19605846 Free PMC article.
-
The C76R transmembrane activator and calcium modulator cyclophilin ligand interactor mutation disrupts antibody production and B-cell homeostasis in heterozygous and homozygous mice.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011 May;127(5):1253-9.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2011.02.037. Epub 2011 Mar 31. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21458042
-
Transmembrane activator and calcium-modulator and cyclophilin ligand interactor mutations in common variable immunodeficiency.Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008 Dec;8(6):520-6. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0b013e3283141200. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18978466 Review.
-
The C104R mutant impairs the function of transmembrane activator and calcium modulator and cyclophilin ligand interactor (TACI) through haploinsufficiency.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010 Dec;126(6):1234-41.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2010.08.017. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20889194 Free PMC article.
-
Genetics of common variable immunodeficiency: role of transmembrane activator and calcium modulator and cyclophilin ligand interactor.Int J Immunogenet. 2015 Aug;42(4):239-53. doi: 10.1111/iji.12217. Epub 2015 Jun 19. Int J Immunogenet. 2015. PMID: 26096648 Review.
Cited by
-
The five dimensions of B cell tolerance.Immunol Rev. 2019 Nov;292(1):180-193. doi: 10.1111/imr.12813. Epub 2019 Oct 14. Immunol Rev. 2019. PMID: 31609002 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rare TACI Mutation in a 3-Year-Old Boy With CVID Phenotype.Front Pediatr. 2019 Oct 15;7:418. doi: 10.3389/fped.2019.00418. eCollection 2019. Front Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 31681716 Free PMC article.
-
TNFRSF13B genotypes control immune-mediated pathology by regulating the functions of innate B cells.JCI Insight. 2021 Sep 8;6(17):e150483. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.150483. JCI Insight. 2021. PMID: 34283811 Free PMC article.
-
TNFRSF13B polymorphisms counter microbial adaptation to enteric IgA.JCI Insight. 2021 Jul 22;6(14):e148208. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.148208. JCI Insight. 2021. PMID: 34111031 Free PMC article.
-
TNFRSF13B Diversification Fueled by B Cell Responses to Environmental Challenges-A Hypothesis.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 17;12:634544. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.634544. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33679786 Free PMC article.
References
-
- von Bulow GU, Bram RJ. NF-AT activation induced by a CAML-interacting member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily. Science. 1997;278:138–41. - PubMed
-
- Yan M, Marsters SA, Grewal IS, Wang H, Ashkenazi A, Dixit VM. Identification of a receptor for BLyS demonstrates a crucial role in humoral immunity. Nat Immunol. 2000;1:37–41. - PubMed
-
- Mackay F, Schneider P, Rennert P, Browning J. BAFF AND APRIL: A Tutorial on B Cell Survival. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:231–64. - PubMed
-
- Seshasayee D, Valdez P, Yan M, Dixit VM, Tumas D, Grewal IS. Loss of TACI causes fatal lymphoproliferation and autoimmunity, establishing TACI as an inhibitory BLyS receptor. Immunity. 2003;18:279–88. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

