A basal cell defect promotes budding of prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia
- PMID: 27609833
- PMCID: PMC5394777
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.188177
A basal cell defect promotes budding of prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia
Abstract
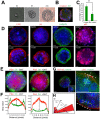
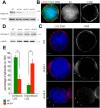
Basal cells in a simple secretory epithelium adhere to the extracellular matrix (ECM), providing contextual cues for ordered repopulation of the luminal cell layer. Early high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (HG-PIN) tissue has enlarged nuclei and nucleoli, luminal layer expansion and genomic instability. Additional HG-PIN markers include loss of α6β4 integrin or its ligand laminin-332, and budding of tumor clusters into laminin-511-rich stroma. We modeled the invasive budding phenotype by reducing expression of α6β4 integrin in spheroids formed from two normal human stable isogenic prostate epithelial cell lines (RWPE-1 and PrEC 11220). These normal cells continuously spun in culture, forming multicellular spheroids containing an outer laminin-332 layer, basal cells (expressing α6β4 integrin, high-molecular-weight cytokeratin and p63, also known as TP63) and luminal cells that secrete PSA (also known as KLK3). Basal cells were optimally positioned relative to the laminin-332 layer as determined by spindle orientation. β4-integrin-defective spheroids contained a discontinuous laminin-332 layer corresponding to regions of abnormal budding. This 3D model can be readily used to study mechanisms that disrupt laminin-332 continuity, for example, defects in the essential adhesion receptor (β4 integrin), laminin-332 or abnormal luminal expansion during HG-PIN progression.
Keywords: Integrin; Laminin; Neoplasia; Prostate; Spheroids.
© 2017. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Unique expression pattern of the alpha6beta4 integrin and laminin-5 in human prostate carcinoma.Prostate. 2001 Feb 15;46(3):240-8. doi: 10.1002/1097-0045(20010215)46:3<240::aid-pros1029>3.0.co;2-0. Prostate. 2001. PMID: 11170153 Free PMC article.
-
The role of alpha 6 beta 1 integrin and EGF in normal and malignant acinar morphogenesis of human prostatic epithelial cells.Mutat Res. 2001 Sep 1;480-481:209-17. doi: 10.1016/s0027-5107(01)00201-9. Mutat Res. 2001. PMID: 11506815
-
The alpha 6 beta 1 and alpha 6 beta 4 integrins in human prostate cancer progression.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1995 Sep;14(3):219-28. doi: 10.1007/BF00690293. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1995. PMID: 8548870 Review.
-
Downregulation of the beta4 integrin subunit in prostatic carcinoma and prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia.Hum Pathol. 1998 Apr;29(4):311-8. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(98)90109-5. Hum Pathol. 1998. PMID: 9563778
-
Natural history of prostatic carcinoma: the pathologist's perspective.Recent Results Cancer Res. 2007;175:9-24. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-40901-4_2. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17432551 Review.
Cited by
-
The Blood-prostate Barrier: An Obstacle to Drug Delivery into the Prostate.Curr Drug Deliv. 2025;22(4):401-412. doi: 10.2174/1567201821666230807152520. Curr Drug Deliv. 2025. PMID: 37550915 Review.
-
Centrosome loss results in an unstable genome and malignant prostate tumors.Oncogene. 2020 Jan;39(2):399-413. doi: 10.1038/s41388-019-0995-z. Epub 2019 Sep 2. Oncogene. 2020. PMID: 31477840
-
Digital image analysis using video microscopy of human-derived prostate cancer vs normal prostate organoids to assess migratory behavior on extracellular matrix proteins.Front Oncol. 2023 Jan 13;12:1083150. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1083150. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36727054 Free PMC article.
-
Glyoxalase 1 Expression as a Novel Diagnostic Marker of High-Grade Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia in Prostate Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jul 19;13(14):3608. doi: 10.3390/cancers13143608. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34298821 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of α6β4 Integrin-Mediated Hemidesmosomes Promotes Prostate Epithelial Cell Migration by Stimulating Focal Adhesion Dynamics.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jul 7;10:886569. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.886569. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35874837 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonkhoff H. (1996). Role of the basal cells in premalignant changes of the human prostate: a stem cell concept for the development of prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. 30, 201-205. - PubMed
-
- Bostwick D. G. (1996a). Progression of prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia to early invasive adenocarcinoma. Eur. Urol. 30, 145-152. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

