The Streptococcus pneumoniae pezAT Toxin-Antitoxin System Reduces β-Lactam Resistance and Genetic Competence
- PMID: 27610103
- PMCID: PMC4997998
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01322
The Streptococcus pneumoniae pezAT Toxin-Antitoxin System Reduces β-Lactam Resistance and Genetic Competence
Abstract
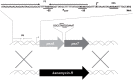
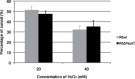
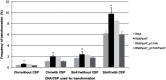
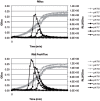
Chromosomally encoded Type II Toxin-Antitoxin operons are ubiquitous in bacteria and archaea. Antitoxins neutralize the toxic effect of cognate Toxins by protein-protein interactions and sequestering the active residues of the Toxin. Toxins target essential bacterial processes, mostly translation and replication. However, one class apart is constituted by the PezAT pair because the PezT toxin target cell wall biosynthesis. Here, we have examined the role of the pezAT toxin-antitoxin genes in its natural host, the pathogenic bacterium Streptococcus pneumoniae. The pezAT operon on Pneumococcal Pathogenicity Island 1 was deleted from strain R6 and its phenotypic traits were compared with those of the wild type. The mutant cells formed shorter chains during exponential phase, leading to increased colony-forming units. At stationary phase, the mutant was more resilient to lysis. Importantly, the mutant exhibited higher resistance to antibiotics targeting cell walls (β-lactams), but not to antibiotics acting at other levels. In addition, the mutants also showed enhanced genetic competence. We suggest that PezAT participates in a subtle equilibrium between loss of functions (resistance to β-lactams and genetic competence) and gain of other traits (virulence).
Keywords: Streptococcus pneumoniae; antibiotic resistance; genetic competence; genetic transformation; pezAT; toxin–antitoxin.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Streptococcus pneumoniaeyefM-yoeB and relBE Toxin-Antitoxin Operons Participate in Oxidative Stress and Biofilm Formation.Toxins (Basel). 2018 Sep 18;10(9):378. doi: 10.3390/toxins10090378. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30231554 Free PMC article.
-
Assembly dynamics and stability of the pneumococcal epsilon zeta antitoxin toxin (PezAT) system from Streptococcus pneumoniae.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jul 9;285(28):21797-806. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.126250. Epub 2010 May 4. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20442221 Free PMC article.
-
Type II bacterial toxin-antitoxins: hypotheses, facts, and the newfound plethora of the PezAT system.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2023 Sep 5;47(5):fuad052. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuad052. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2023. PMID: 37715317 Free PMC article.
-
Keeping the Wolves at Bay: Antitoxins of Prokaryotic Type II Toxin-Antitoxin Systems.Front Mol Biosci. 2016 Mar 22;3:9. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2016.00009. eCollection 2016. Front Mol Biosci. 2016. PMID: 27047942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toxin-Antitoxin Systems in Clinical Pathogens.Toxins (Basel). 2016 Jul 20;8(7):227. doi: 10.3390/toxins8070227. Toxins (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27447671 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Towards Exploring Toxin-Antitoxin Systems in Geobacillus: A Screen for Type II Toxin-Antitoxin System Families in a Thermophilic Genus.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 22;20(23):5869. doi: 10.3390/ijms20235869. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31771094 Free PMC article.
-
Clonal Complex 12 Serotype Ib Streptococcus agalactiae Strain Causing Complicated Sepsis in Neonates: Clinical Features and Genetic Characteristics.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Feb 14;11(1):e0377822. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03778-22. Epub 2022 Dec 8. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36475780 Free PMC article.
-
The Mobilome-Enriched Genome of the Competence-Deficient Streptococcus pneumoniae BM6001, the Original Host of Integrative Conjugative Element Tn5253, Is Phylogenetically Distinct from Historical Pneumococcal Genomes.Microorganisms. 2023 Jun 23;11(7):1646. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11071646. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37512819 Free PMC article.
-
The ng_ζ1 toxin of the gonococcal epsilon/zeta toxin/antitoxin system drains precursors for cell wall synthesis.Nat Commun. 2018 Apr 27;9(1):1686. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03652-8. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29703974 Free PMC article.
-
The Streptococcus pneumoniaeyefM-yoeB and relBE Toxin-Antitoxin Operons Participate in Oxidative Stress and Biofilm Formation.Toxins (Basel). 2018 Sep 18;10(9):378. doi: 10.3390/toxins10090378. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30231554 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

