Development of pH Sensitive Nanoparticles for Intestinal Drug Delivery Using Chemically Modified Guar Gum Co-Polymer
- PMID: 27610149
- PMCID: PMC4986109
Development of pH Sensitive Nanoparticles for Intestinal Drug Delivery Using Chemically Modified Guar Gum Co-Polymer
Abstract
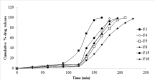
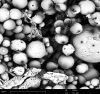
The aim of the research work was to chemically modify guargum (GG) as a pH sensitive co-polymer and formulating intestinal targeting ESO nanoparticles (NPs) using the synthesized co-polymer. Poly acrylamide-grafted-guar gum (PAAm-g-GG) co-polymer was synthesized by free radical polymerization. Chemical modification of PAAm-g-GG by alkaline hydrolysis results in formation of a pH-sensitive co-polymer. The effect of GG and acryl amide (AAm) on grafting was studied. Esomeprazole magnesium (ESO) loaded pH sensitive NPs were prepared by nano-emulsification polymer crosslinking method and characterized. Sixteen formulations were prepared and the concentration of process variables wasvaried to obtain nanoparticles of 200-600 nm. The NPs were found to be homogenous in size distribution. The encapsulation efficiency and drug loading ranged from 33.2% to 50.1% and 12.2% to 17.2% respectively. Particle size, encapsulation efficiency and drug loading increasedalong with co-polymer concentration. In-vitro release studies at pH 1.2 for 2 h, followed by pH 6.8 showed that environment pH significantly affected the drug release. SEM has shown that NPsare spherical with smooth surface. The pH sensitive PAAm-g-GGNPs resisted the initial release of the drug from the drug loaded NPs in acidic pH and delayed the release process to a longer period in alkaline environment.
Keywords: Esomeprazole; PAAm-g-GG; guar gum; intestinal drug delivery; pH sensitive nanoparticles.
Figures
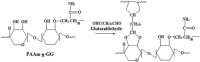
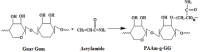

Similar articles
-
Modified guar gum matrix tablet for controlled release of diltiazem hydrochloride.J Control Release. 2004 Mar 24;95(3):567-77. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2003.12.019. J Control Release. 2004. PMID: 15023467
-
Novel pH-sensitive IPNs of polyacrylamide-g-gum ghatti and sodium alginate for gastro-protective drug delivery.Int J Biol Macromol. 2015 Apr;75:133-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.01.029. Epub 2015 Jan 23. Int J Biol Macromol. 2015. PMID: 25623023
-
pH sensitive alginate-guar gum hydrogel for the controlled delivery of protein drugs.Int J Pharm. 2007 Apr 20;335(1-2):123-129. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2006.11.009. Epub 2006 Nov 7. Int J Pharm. 2007. PMID: 17147980
-
Enteric delivery of ketoprofen through functionally modified poly(acrylamide-grafted-xanthan)-based pH-sensitive hydrogel beads: preparation, in vitro and in vivo evaluation.J Drug Target. 2008 Feb;16(2):167-77. doi: 10.1080/10611860701792399. J Drug Target. 2008. PMID: 18274937
-
Research Progress of a Pesticide Polymer-Controlled Release System Based on Polysaccharides.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Jun 25;15(13):2810. doi: 10.3390/polym15132810. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37447458 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Enzyme-Responsive Nanoparticles and Coatings Made from Alginate/Peptide Ciprofloxacin Conjugates as Drug Release System.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 May 29;10(6):653. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10060653. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34072352 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gaurav T, Ruchi T, Pranay W, Ankita W, Awani KR. Primary and novel approaches for colon targeted drug delivery -A review. Int J Drug Del. 2010;2:01–11.
-
- Regis C, Laurence P, Vincent P, Christine J, David JB, Yves-Jacques S, Schneider , Veronique P. Drug Delivery to inflamed colon by nanoparticles: Comparison of different strategies. Int J Pharm. 2013;440:3–12. - PubMed
-
- Raj Kumar S, Akanksha T. Carbohydrate polymers: Applications and recent advances in delivering drugs to the colon. Carbohydr Polym. 2012;88:399–416.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
