Development of pH Sensitive Nanoparticles for Intestinal Drug Delivery Using Chemically Modified Guar Gum Co-Polymer
- PMID: 27610149
- PMCID: PMC4986109
Development of pH Sensitive Nanoparticles for Intestinal Drug Delivery Using Chemically Modified Guar Gum Co-Polymer
Abstract
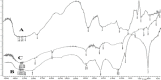
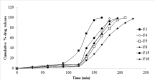
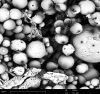
The aim of the research work was to chemically modify guargum (GG) as a pH sensitive co-polymer and formulating intestinal targeting ESO nanoparticles (NPs) using the synthesized co-polymer. Poly acrylamide-grafted-guar gum (PAAm-g-GG) co-polymer was synthesized by free radical polymerization. Chemical modification of PAAm-g-GG by alkaline hydrolysis results in formation of a pH-sensitive co-polymer. The effect of GG and acryl amide (AAm) on grafting was studied. Esomeprazole magnesium (ESO) loaded pH sensitive NPs were prepared by nano-emulsification polymer crosslinking method and characterized. Sixteen formulations were prepared and the concentration of process variables wasvaried to obtain nanoparticles of 200-600 nm. The NPs were found to be homogenous in size distribution. The encapsulation efficiency and drug loading ranged from 33.2% to 50.1% and 12.2% to 17.2% respectively. Particle size, encapsulation efficiency and drug loading increasedalong with co-polymer concentration. In-vitro release studies at pH 1.2 for 2 h, followed by pH 6.8 showed that environment pH significantly affected the drug release. SEM has shown that NPsare spherical with smooth surface. The pH sensitive PAAm-g-GGNPs resisted the initial release of the drug from the drug loaded NPs in acidic pH and delayed the release process to a longer period in alkaline environment.
Keywords: Esomeprazole; PAAm-g-GG; guar gum; intestinal drug delivery; pH sensitive nanoparticles.
Figures
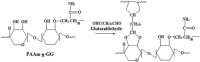
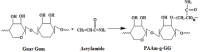

References
-
- Gaurav T, Ruchi T, Pranay W, Ankita W, Awani KR. Primary and novel approaches for colon targeted drug delivery -A review. Int J Drug Del. 2010;2:01–11.
-
- Regis C, Laurence P, Vincent P, Christine J, David JB, Yves-Jacques S, Schneider , Veronique P. Drug Delivery to inflamed colon by nanoparticles: Comparison of different strategies. Int J Pharm. 2013;440:3–12. - PubMed
-
- Raj Kumar S, Akanksha T. Carbohydrate polymers: Applications and recent advances in delivering drugs to the colon. Carbohydr Polym. 2012;88:399–416.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
