Generating Light from Upper Excited Triplet States: A Contribution to the Indirect Singlet Yield of a Polymer OLED, Helping to Exceed the 25% Singlet Exciton Limit
- PMID: 27610333
- PMCID: PMC4991292
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.201500221
Generating Light from Upper Excited Triplet States: A Contribution to the Indirect Singlet Yield of a Polymer OLED, Helping to Exceed the 25% Singlet Exciton Limit
Abstract
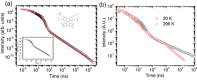
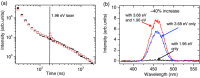
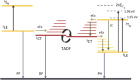
The mechanisms by which light is generated in an organic light emitting diode have slowly been elucidated over the last ten years. The role of triplet annihilation has demonstrated how the "spin statistical limit" can be surpassed, but it cannot account for all light produced in the most efficient devices. Here, a further mechanism is demonstrated by which upper excited triplet states can also contribute to indirect singlet production and delayed fluorescence. Since in a device the population of these TN states is large, this indirect radiative decay channel can contribute a sizeable fraction of the total emission measured from a device. The role of intra- and interchain charge transfer states is critical in underpinning this mechanism.
Keywords: OLED; charge transfer states; delayed fluorescence; reverse intersystem crossing; triplet fusion, triplet–triplet annihilation.
Figures

References
-
- Wohlgenannt M., Tandon K., Mazumdar S., Ramasesha S., Vardeny Z. V., Nature 2001, 409, 494. - PubMed
-
- Monkman A. P., Rothe C., King S. M., Proc. IEEE 2009, 97, 1597.
-
- Hertel D., Bassler H., Guentner R., Scherf U., J. Chem. Phys. 2001, 115, 10007.
-
- Rothe C., Monkman A. P., Phys. Rev. B 2003, 68, 075208.
-
- Baldo M. A., Adachi C., Forrest S. R., Phys. Rev. B 2000, 62, 10967.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
